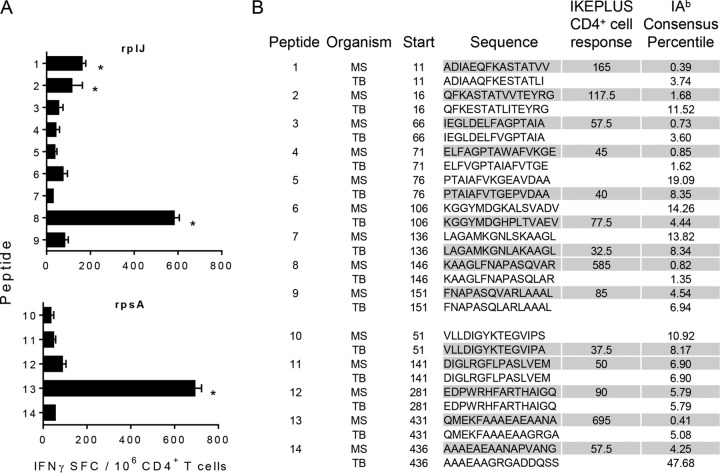
FIG 9.
Identification of CD4+ T cell targets within the RplJ and RpsA ribosomal proteins. Peptides were screened for in silico-predicted binding affinity for I-Ab. These peptides included nine peptides derived from the RplJ protein and five peptides derived from the RpsA protein. (A) IFN-γ ELISPOT responses to selected RplJ and RpsA peptides by CD4+ T cells from IKEPLUS-immunized mice. CD4+ T cells were isolated at 2 weeks postimmunization from spleens of C57BL/6 mice immunized i.v. with 5 × 107 CFU IKEPLUS and assayed by an ELISPOT assay for the production of IFN-γ in response to the 14 peptides (10 μg/ml for each peptide). Asterisks indicate >3 standard deviations above values for replicate wells with no antigen. No responses to individual peptides were detected by using CD4+ T cells from BCG-immunized mice (not shown). Data shown represent mean values and standard deviations for duplicate samples. Data shown are representative of results from two independent experiments. (B) Sequences of both M. tuberculosis (TB) and M. smegmatis (MS) peptides along with the location of their first residue (start) in the RplJ or RpsA protein. The sequences are shown in single-letter amino acid code. Shaded cells represent peptides that were synthesized and analyzed based on the I-Ab consensus percentile. Responses of immune CD4+ T cells to the peptides are summarized as the number of positive cells per 106 CD4+ T cells, quantified by an IFN-γ ELISPOT assay, as shown in panel A.