Figure 3.
Signal-Induced Histone Modifications at TSSs Are Not Transcription Factor or Promoter Specific
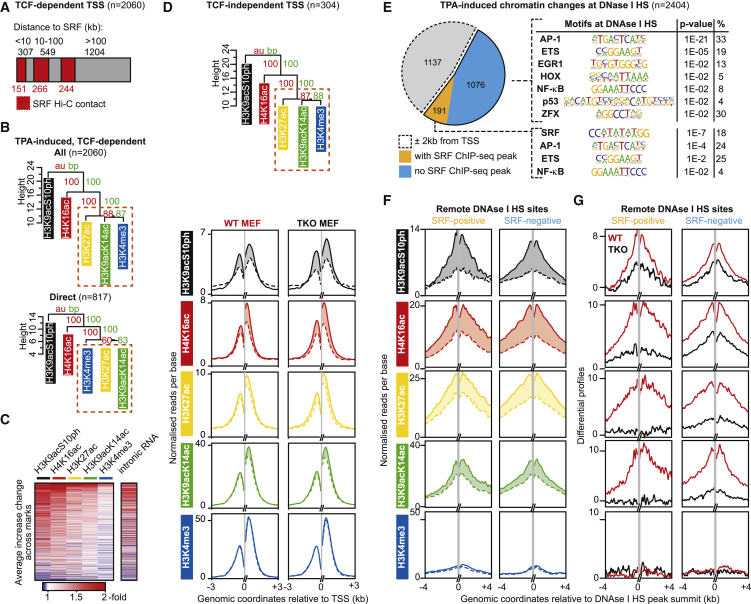
(A) Definition of SRF-linked TSSs exhibiting TCF-dependent TPA-induced histone modifications. TSSs are classified by the closest SRF ChIP-seq peak, with TSSs displaying Hi-C interaction with SRF shaded in red. “Direct” TCF-SRF controlled TSSs (n = 817) are defined as all those within 10 kb of an SRF site or that interact in Hi-C.
(B) Hierarchy of TPA-induced histone modification changes at all TCF-dependent TSS regions (top) and direct TCF-dependent TSSs (bottom) displayed as in Figure 1B (see also Figure S2A).
(C). Heatmap representation of the ChIP-seq signals at the 817 direct TCF-SRF controlled TSS regions, ranked by average fold change, compared with TPA-induced change in RNA synthesis.
(D) Hierarchy of TPA-induced histone modification changes at the 304 TCF-independent TSS regions, with metaprofiles of the modifications, plotted as in Figure 1D, shown below.
(E) Left: classification of the 2,404 DNase I HS sites showing significant changes in ChIP-seq signals. Gray, sites within 2 kb of a TSS; orange, remote sites with SRF ChIP-seq peaks; blue, others. Sequence motifs enriched at remote DNase I HS are shown at the right.
(F) Differential metaprofiles of induced histone modifications at remote DNase I HS sites in wild-type MEFs; shading indicates change upon induction.
(G) Differential metaprofiles of histone modification changes at the remote DNase I HS sites in wild-type (red line) and TKO (black lines) MEFs.