Figure 3.
MOAG-2/LIR-3 Regulates Transcription of Small ncRNAs
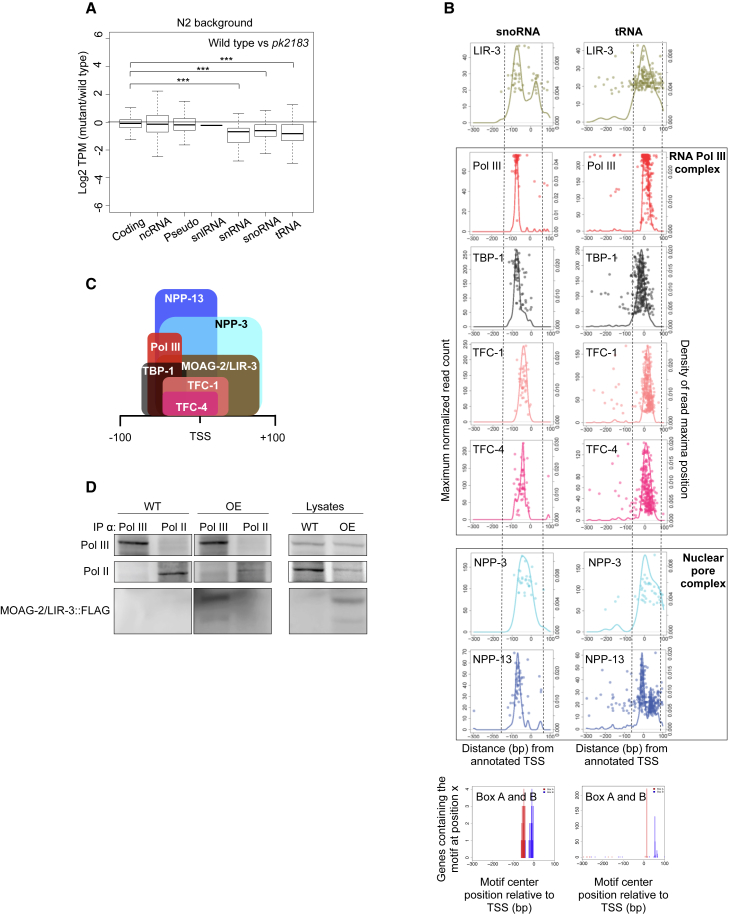
(A) Boxplot showing the relative expression of different gene biotypes in moag-2/lir-3(pk2183) worms relative to the wild-type N2 background. TPM, tags per kilobase million; Coding, protein-coding genes; ncRNA, non-coding RNA; Pseudo, pseudogenes; snRNA, small nuclear RNA; snlRNA, snRNA-like RNA; snoRNA, small nucleolar RNA; tRNA, transfer RNA. The average of three biological replicates is represented and significance was calculated using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S3A.
(B) Positions of ChIP-seq signal maxima relative to TSS (right y axis) with maximum normalized read count (left y axis) for the 51 snoRNA genes and the 290 tRNA genes picked in this study. Bottom box represents the motif position of Box A and Box B relative to snoRNA and tRNA genes. See also Figures S3B and S3C.
(C) Diagram showing the positions of the Pol III factors and that of MOAG-2/LIR-3 as estimated from the data presented in (B).
(D) Co-immunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged MOAG-2/LIR-3 protein by α-Pol II and α-Pol III protein antibodies. IP, immunoprecipitation; WT, wild-type; OE, MOAG-2/LIR-3 overexpression.