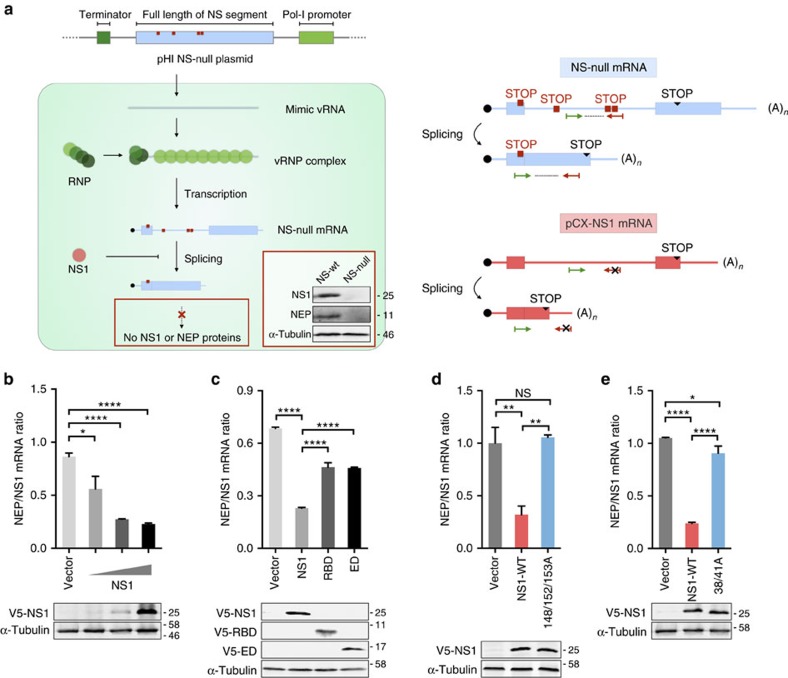
Figure 6. Effect of NS1 on NS mRNA splicing.
(a) Schematic illustration of NS-null replicon system and detection of specific NS mRNAs. (Left panel) Construction of the pHI NS-null plasmid, which contains multiple stop codons (red squares). NS vRNA mimics were generated from pHI NS-null plasmid by pol-I and incorporated into RNP complexes. NS vRNA mimics were further transcribed into NS-null spliced and unspliced mRNAs by the viral polymerase complex and host machinery. Owing to the presence of stop codons, neither unspliced or spliced NS-null mRNAs could be translated into complete NS1 or NEP proteins, respectively. (Right panel) Specific primers (arrowheads) for detection of NS-null mRNA and its spliced form, but not mRNA expressed from the pCX-NS1 plasmid, in RT–qPCR assay. The primer sets only detect NS-null mRNA and not NS1 mRNA expressed from the pCX-NS1 plasmid, as the reverse primer (red) is base pair matched to the introduced stop codons and not WT sequences. Meanwhile, the antisense primer for spliced NS-null mRNA anneals to the coding region of NEP that is not present in NS1 mRNA. Validation of NS1 or NEP protein expression when pHI-H7N9-NS or pHI-H7N9-NS-null are co-transfected together with the RNP polymerase complex, is shown by IB using antibodies against NS1, NEP or α-tubulin (insert, left panel). (b) HEK293T cells were transfected with pHI-NS-null and RNP, together with increasing amounts of V5-NS1 (0.5, 5 and 50 ng). (c–e) HEK293T cells were transfected with pHI-NS-null and RNP, together with either vector (control) or WT, RBD or effector domain (ED) versions of V5-NS1 (c), WT or 148/152/153A mutant of V5-NS1 (d), or WT or R38A/K41A V5-NS1 (e). Total RNA from transfected cells in b,c,d and e was isolated and the splicing ratio of NS-null mRNA was measured by RT–qPCR. Levels of the various versions of NS1 and tubulin (control) were analysed by IB with antibodies against V5 and tubulin, respectively. Error bars represent mean±s.d. (n=3). Statistical significance was analysed by Student's t-test: *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ****P<0.0001.