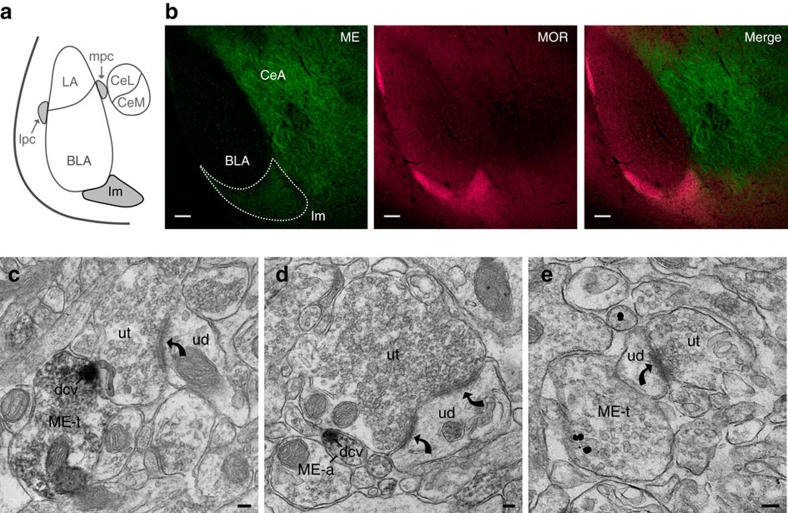
Figure 1. Met-enkephalin expressed within the main ITC island is positioned to modulate excitatory synapses.
(a) Schematic of amygdala subdivisions. ITC islands are shaded in grey. BLA, basolateral amygdala; CeL, lateral central amygdala and CeM, medial central amygdala make up the central amygdala (CeA); Im, Main ITC island; lpc, lateral ITC; mpc, medial ITC. (b) Single confocal images in the amygdala (Bregma −2.00 mm) of ME (green), MOR (magenta) and the two merged channels. Im is outlined by the dashed line. Scale bars, 100 μm. (c–e) electron micrographs showing: (c) ME immunoreactivity is located in an axon terminal (ME-t) and concentrated in a dense core vesicle (dcv) that is directly apposed to an unlabeled terminal (ut) that forms an asymmetric synapse (curved arrow) with an unlabelled dendrite (UD). (d) An, unmyelinated axon (ME-a) contains a dense core vesicle that is immunoreactive for ME and is apposed to an unlabeled axon terminal (ut) that forms a perforated asymmetric synapse (curved arrows) with an unlabelled dendrite (UD). (e) ME immunogold immunoreactivity is located in an axon terminal (ME-t) apposed to an unlabelled dendrite (ud) that receives an asymmetric synapse (curved arrow) from an unlabelled terminal (ut). Scale bars, 100 nm.