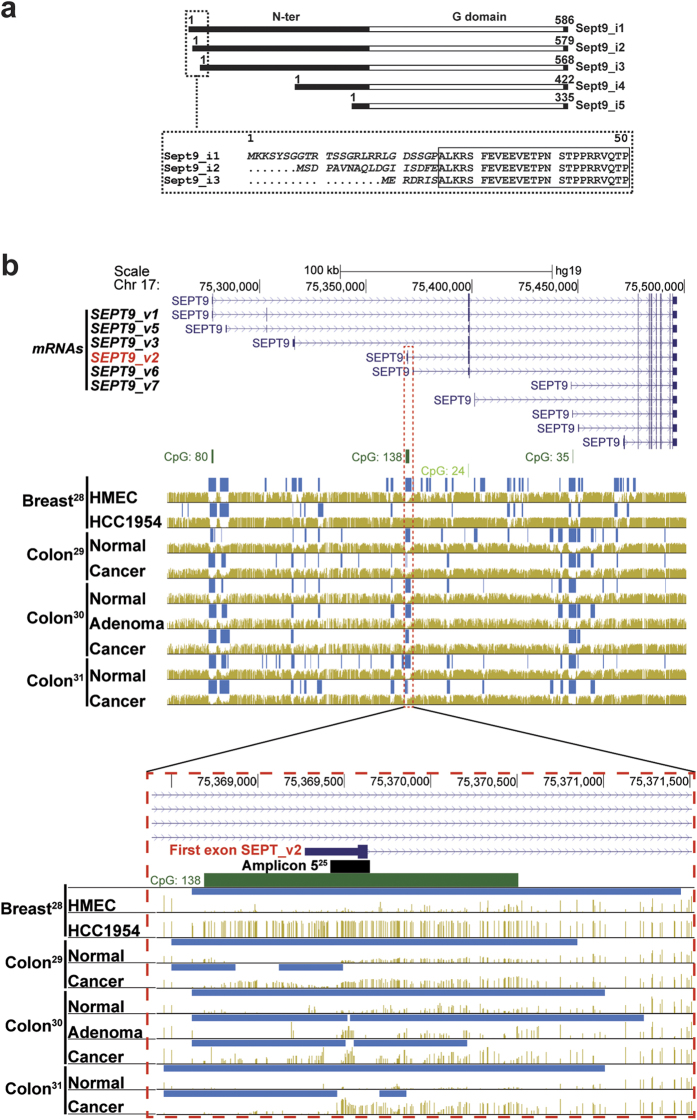
Figure 1. Differential CpG methylation levels of the SEPT9 gene in carcinoma vs normal epithelia.
(a) Sept9 isoform proteins differ by their N-terminal domain; long isoforms, Sept9_i1,_i2,_i3 differ from each other by their starting amino acid sequences (indicated in italic and see Supplementary Fig. S1 for sequence details). (b) Top panel presents the human SEPT9 gene locus on Chr 17 with 11 alternatively spliced mRNA variants having in common the last 9 exons; six of these transcripts are present in breast tissues24, SEPT9_v1, _v2,_v3,_v5,_v6 and_v7, coding for Sept9_i1,_i2,_i3,_i4,_i4 and_i5 isoforms, respectively. Middle panel displays the position of CpG islands (dark green >300 bases; 200< light green <300 bases), hypo-methylated regions (dark blue bars on top of corresponding genome) and methylated CpGs (golden brown vertical lines whose height is proportional to CpG methylation level). Four groups of human methylome datasets are presented: first set, HMEC (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells, primary cell line) vs HCC1954 (grade 3, ductal carcinoma cell line)28; second set, normal colon and colon cancer derived primary epithelial cell lines29; third set, normal colon, colon adenoma and tumor biopsies30; fourth set, normal colon and colon cancer biopsies31. Bottom panel is the zoomed region delineated by a dashed red frame including the large CpG island 138 and the first exon of SEPT9_v2; the location of the differentially methylated amplicon identified by Wasserkort et al.25 in microdissected colon cancer cells is represented by a black bar on top of CpG 138 island (dark green bar). Public bisulfite-seq datasets were extracted from the MethBase methylome database using the UCSC Genome Browser on Human Feb. 2009 (GRCh37/hg19) assembly and the MethPipe software package (smithlabresearg.org).