Figure 4. Sept9_i2 inhibits MCF7 cell migration.
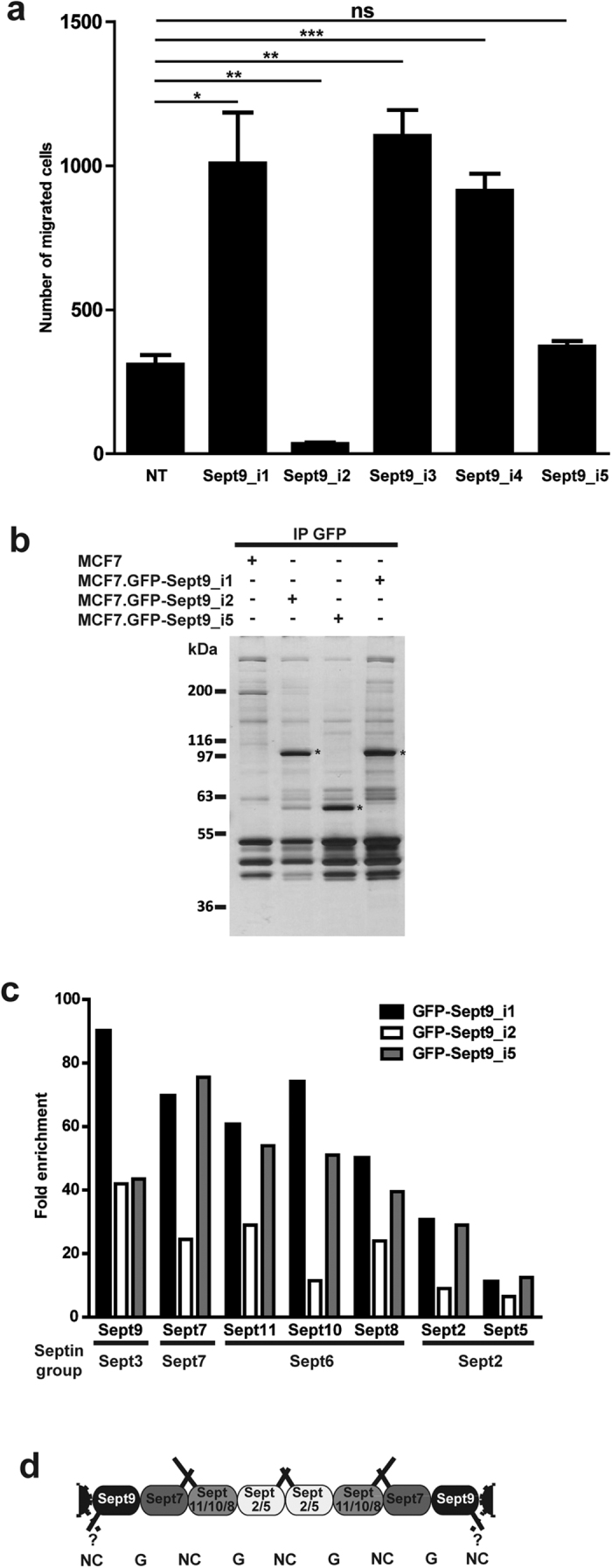
(a) Migration of MCF7 cell lines stably expressing one of Sept9 isoforms was measured in a transwell assay. The reference migrated cell number was of non-transfected (NT) MCF7 parental cell lines. Means and standard deviations from three independent experiments are presented; t-test, *p value < 0.05, **p value < 0.01, ***p value < 0.001. (b-d) Identification of the protein partners of specific Sept9 isoforms. (b) Silver stained SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP-pull down performed on extracts from MCF7 cells stably expressing either GFP-Sept9_i1 or_i2 or_i5, used for mass spectrometry analyses. Extracts from non-transfected MCF7 cells were used as a control. (c) Mass spectrometry analyses identified only other septin family members. Results are expressed as means of total ion intensity signal-based enrichment ratio of proteins in GFP-pulldowns relative to control from two independent experiments. Sept9-associated septins were assembled by septin groups. The average ratio for each septin was consistent with its position in the septin tetramer. The detailed results of two independent pull-downs are presented in Supplementary Table S1 and the Vulcano plots from one pull-down are presented in Supplementary Fig. S3. (d) Scheme of septin octameric polymer with the different septins identified in MCF7 cells with known G domain-G domain (G) and N-terminus/C-terminus-N-terminus/C-terminus (NC) interactions. Septin coil-coiled C-terminal interactions and Sept9 long N-termini putative interactions are represented as solid bars at the top and the bottom of the polymer, respectively.
