Fig. 5.
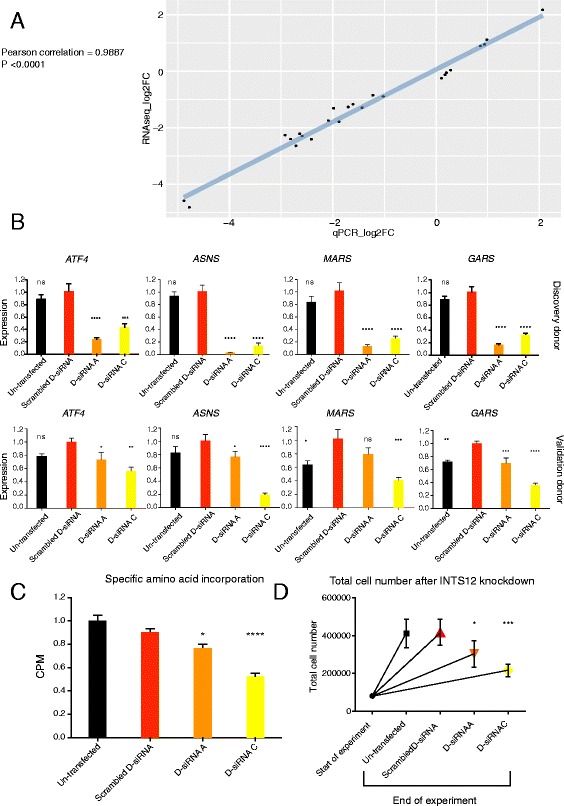
Technical, biological and phenotypic validation of the INTS12 knockdown impact on the protein synthesis pathways. a Technical validation of RNAseq findings by qPCR. Differences in gene expression derived from RNAseq strongly and significantly correlate with differences in gene expression derived from qPCR. Validation assays were performed on the same samples that were used for RNAseq study. b Biological validation of downregulation of genes belonging to cytosolic tRNA aminoacylation and PERK pathways in HBECs from the discovery donor (used in RNAseq) and in an additional donor (validation donor). Statistical tests were performed comparing to scrambled D-siRNA control: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Individual ∆∆Ct gene expressions are GAPDH normalized and relative to the mean of the scrambled D-siRNA condition. c Amino acid incorporation measured by counts per methionine (CPM) in 120 h since the start of RNAi radiolabelling experiment. Statistical tests were performed comparing to scrambled D-siRNA control: *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. Individual CPM values are normalized to the amount of total protein and are shown as relative to the mean of the un-transfected condition. d HBEC counts at the beginning and at the end of 120 h INTS12 knockdown experiment. Statistical tests were performed comparing to scrambled D-siRNA control: *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001
