Fig. 5.
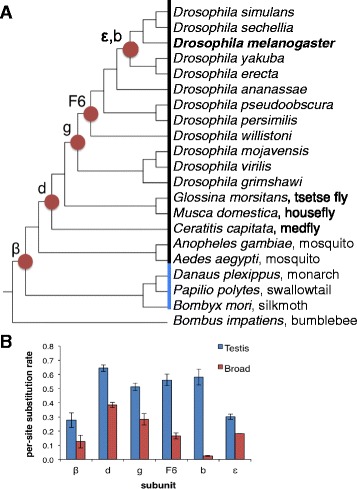
Phylogeny and evolution of Knon and other ATP synthase subunit paralogs in insects. a The six ATP synthase subunits encoded by two paralogs in D. melanogaster have widely varying phylogenetic origins, determined by comparisons among insect genome sequences (black, Diptera; blue, Lepidoptera) deposited in NCBI. Circles indicate the most recent common ancestor that contained both paralogs. b Testis-enriched subunits have acquired more amino acid substitutions relative to a recent outgroup than broadly expressed subunits. The testis-specific ortholog of each subunit was inferred based on sequence similarity to D. melanogaster orthologs, which were in all cases unambiguous. The average per-site amino acid substitution rate for each subunit type relative to the most recent outgroup of the gene duplication was calculated from a Clustal Omega alignment [76]. Error bars indicate standard deviation among the species analyzed
