Fig. 4.
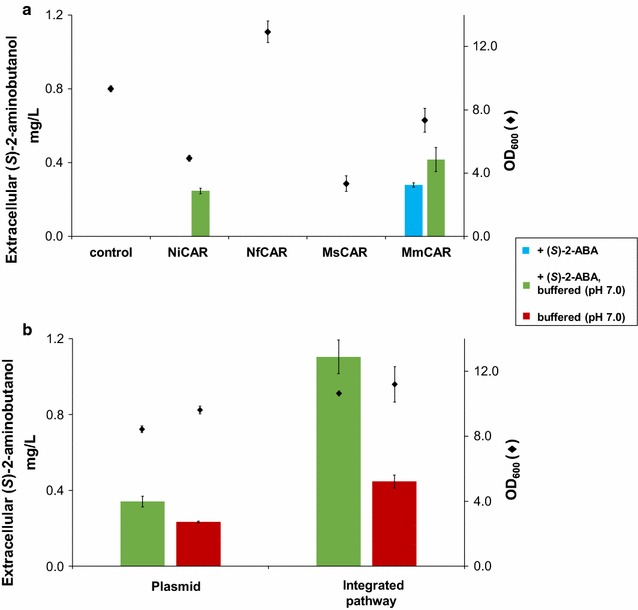
Extracellular accumulation of (S)-2-aminobutanol in S. cerevisiae. a Yeasts were transformed with plasmids harboring the sequences encoding a threonine deaminase and EcGDH’, in combination with different carboxylic acid reductases. PPTases were either from Mycobacterium smegmatis (for MsCAR) or from Bacillus subtilis (SFP) for all other CARs. The aldehyde reductase for the last step of the pathway was derived from E. coli. Engineered yeasts were incubated for 72 h in selective SC medium containing 0.5 g/L (S)-2-aminobutyric acid (+(S)-2-ABA). The medium was either buffered to pH 7 (green bars), or supplied unbuffered (blue bar). Supernatants were analyzed for (S)-2-aminobutanol production. b All five pathway genes (CAR from Mycobacterium marinum) were integrated into chromosome XI-2. Yeasts were incubated for 72 h in selective SC medium buffered to pH 7, and were either supplied with 0.5 g/L (S)-2-aminobutyric acid (green bars), or were grown without additional (S)-2-aminobutyric acid supply (red bars). Diamonds indicate OD600 after 72 h of growth (all data: mean ± SD, n = 3)
