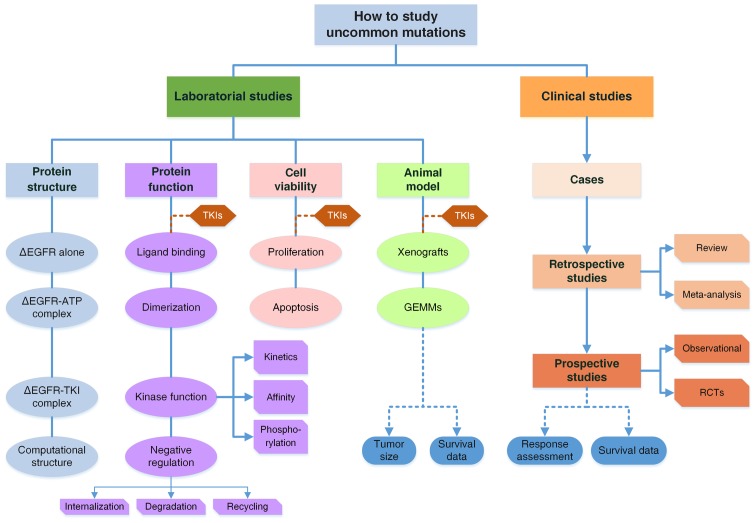
Figure 3.
A comprehensive model to study uncommon mutations in EGFR. The system is comprised of both basic and clinical studies. Clinical studies include three parts: Case reports and series; Retrospective studies are reviews and meta-analyses to combine the data of RR and survival of patients with the G719X mutation; Prospective studies of observational ones or randomized controlled trials. There are two major issues in clinical studies: response to TKIs and survival data of patients. Laboratory studies are organized from mutant protein structures to functional changes, cell viability and animal models. Structural analyses by crystal diffraction or computational simulation determine the structures of mutant EGFR, EGFR-ATP complexes and EGFR-TKI complexes, to elucidate functional changes. Functional studies are categorized into four parts from the perspective of EGFR activation, including ligand biding, dimerization, kinase activity and downregulation, while the latter two are further subdivided as illustrated. For cell viability, the two aspects of proliferation and apoptosis are considered. Animal models involve GEMMs and tumor-cell inoculated xenografts including PDX models, which are discussed in terms of tumor sizes and animal survival. TKI treatment is introduced into all experiments on three levels. With basic and clinical studies integrated together, a complete evidence system is formed to draw conclusions regarding the pathogenic and pharmacological properties of uncommon mutations with high reliability. ∆EGFR, mutant EGFR.