Figure 3.
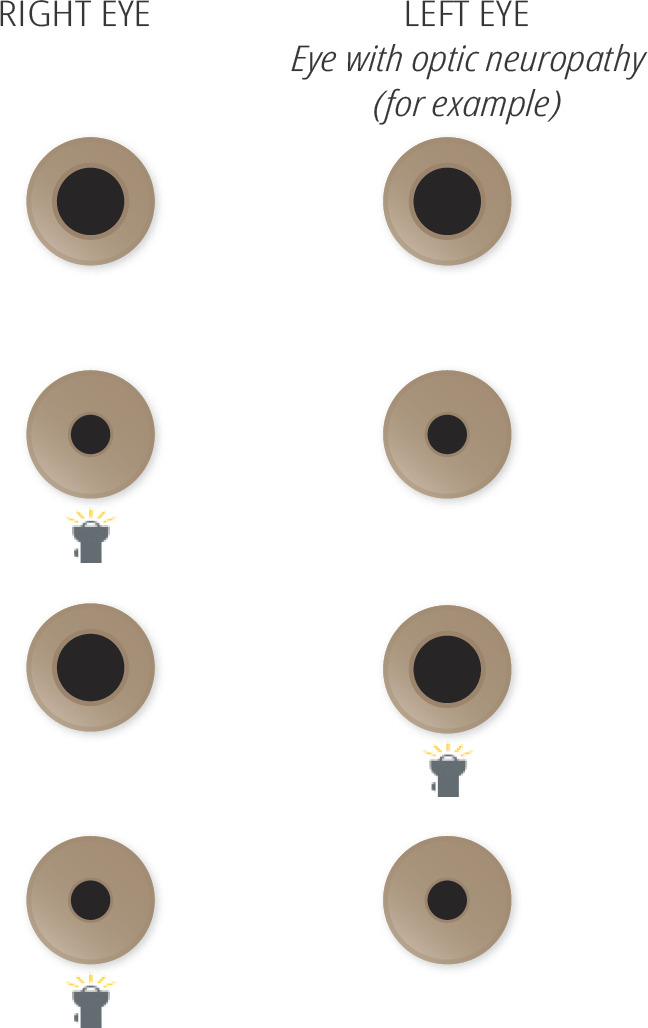
Swinging-light test – left RAPD
Illumination of the (more) normal right eye causes both pupils to constrict. When the light is moved to the (more) abnormal left eye (e.g. with optic neuropathy), both pupils dilate (constrict less), the left pupil dilating despite the light being shone directly at it. Returning the light to the (relatively) normal right eye results in constriction of both pupils again.
