Figure 4.
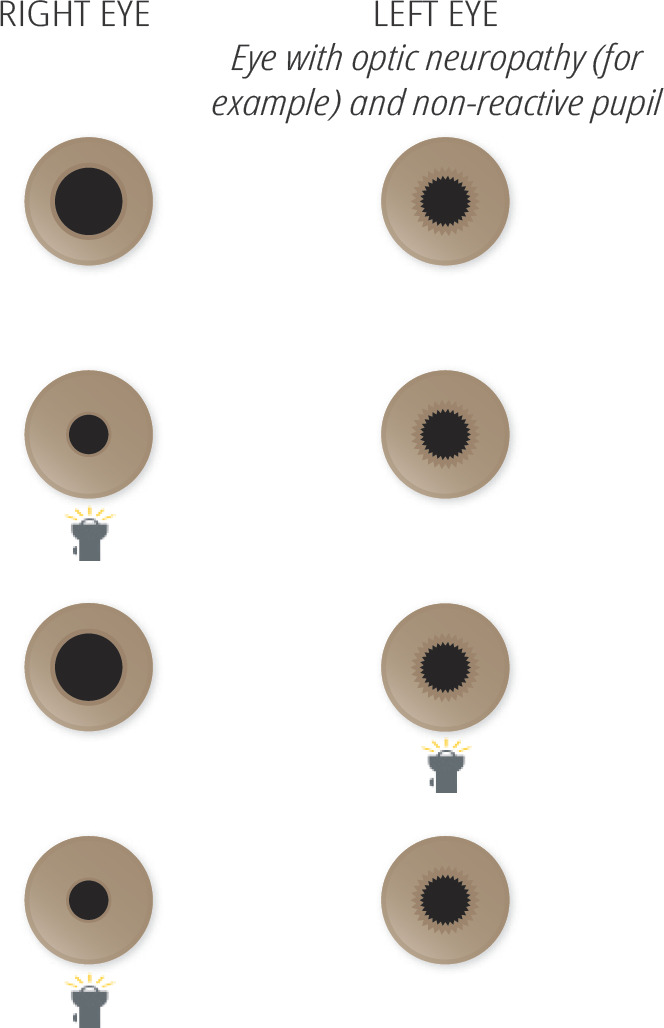
Swinging-light test: left RAPD + non-reactive left pupil
Illumination of the relatively normal right eye causes only right pupil constriction. When the light is moved to the abnormal left eye (e.g. fixed pupil and optic neuropathy), the right pupil dilates (constricts less). Returning the light to the right eye results in constriction of the right pupil again. In this situation it is only necessary to observe the eye with the reactive pupil in order to identify an RAPD.
