Figure 1.
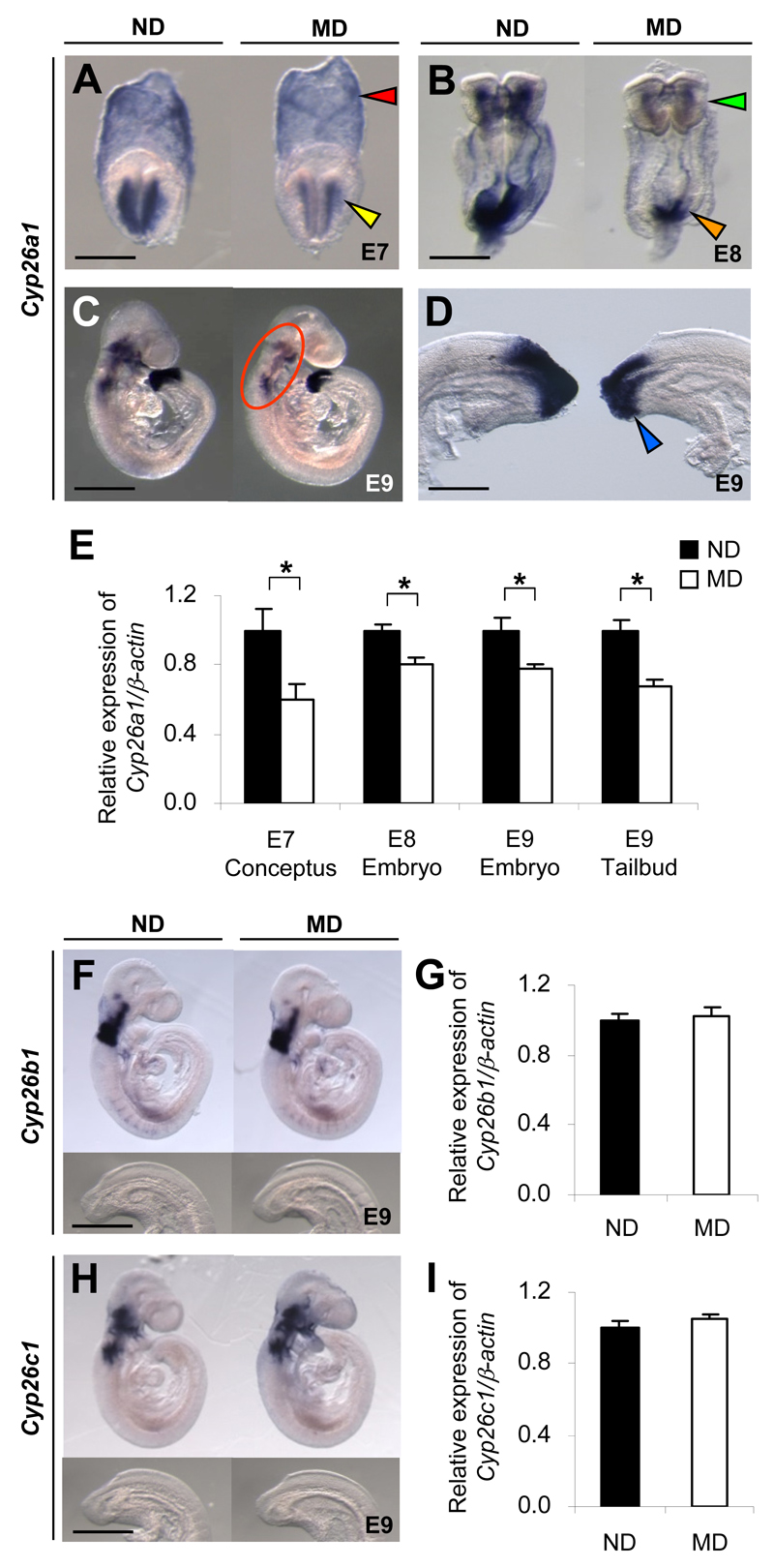
Embryos of diabetic mice exhibit specific downregulation of Cyp26a1. A-D, F, and H: Whole-mount in situ hybridization patterns of Cyp26 genes in embryos of MD mice compared with those of ND mice. Cyp26a1 mRNA transcripts are seen in extraembryonic endoderm (red arrowhead) and headfold mesenchyme (yellow arrowhead) of E7 conceptuses (A); cranial mesenchyme (green arrowhead) and caudal neural plate (orange arrowhead) of E8 embryos (B); craniofacial, cervical, and branchial arch mesenchyme (circled) (C); and tailbud (blue arrowhead) of E9 embryos (D). Cyp26b1 (F) and Cyp26c1 (H) are expressed in the cranial but not in the tailbud region of E9 embryos. At least 20 embryos from five or six litters were examined for each group. Scale bar = 0.05 mm (A), 0.1 mm (B), 0.7 mm (C), 0.2 mm (D), 0.7 mm for the whole embryo and 0.35 mm for the caudal region (F and H). E,G, and I: Quantification of mRNA levels of Cyp26a1 (E), Cyp26b1 (G), and Cyp26c1 (I), normalized to β-actin and expressed relative to ND, which was set as 1 (n = 5 from five litters). *P < 0.05, Student t test. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM.