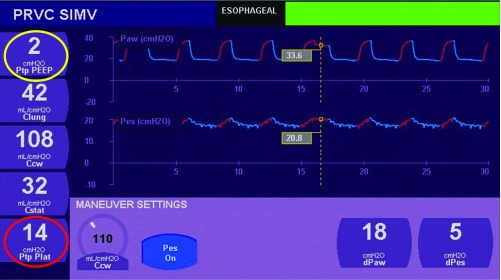
Figure 2. Esophageal and transpulmonary pressures measured in an 8-year-old morbidly obese patient with the Avea ventilator ® from CareFusion.
(1) Transpulmonary pressure (TPP = plateau pressure – esophageal pressure: to calculate TPP, esophageal pressure is used as a surrogate of intrapleural pressure) is 14 cmH 2O at the end of insufflation (red circle). This means that despite a positive plateau pressure of 34 cmH 2O in this obese child, lung parenchyma does not experience much distension (14 cmH 2O) at the end of insufflation. (2) Positive end expiration pressure (PEEP) set on the ventilator is 2 cmH 2O above esophageal pressure (yellow circle). This means that there is minimal risk of lung collapse at the end of expiration. Figure adapted from RM DiBlasi database with permission.