Figure 3. Role of CD44 in the hyperalgesia induced by hyaluronidase or low molecular weight hyaluronan (LMWH).
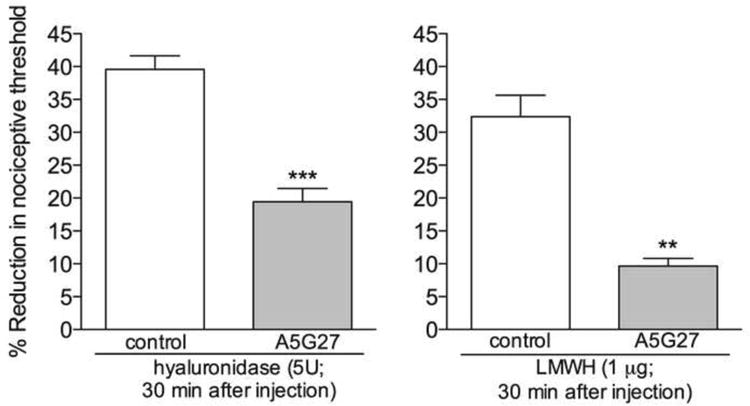
Rats received intradermal injection of vehicle (control) or the CD44 receptor antagonist A5G27 (1 μg) on the dorsum of the hind paw. 10 min later, hyaluronidase (5U, left panel) or LMWH (1 μg, right panel) was injected at the same site. Although mechanical hyperalgesia was observed 30 min after the injection of hyaluronidase or LMWH, in the groups that were pretreated with A5G27 it was significantly attenuated (left panel: t5 = 6.077, *** p = 0.0017; right panel: t5 = 6.644, ** p = 0.0012, when A5G27-treated and the control groups are compared), indicating a role of the CD44 receptor in the hyperalgesia induced by hyaluronidase and LMWH. (Student's t test ; n = 6 paws per group)
