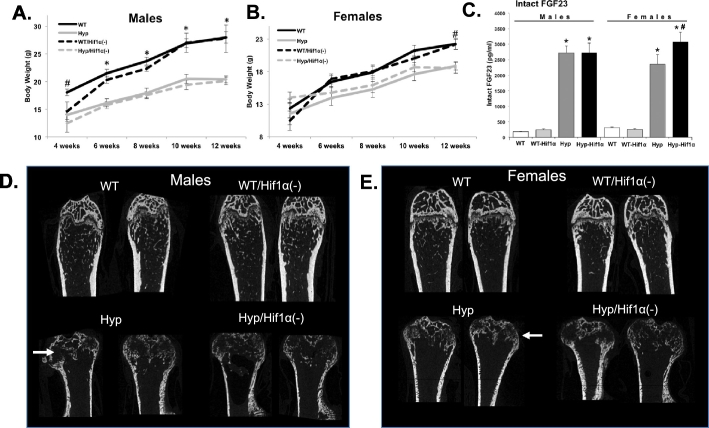
Fig. 2.
Effects of Hif1α(Cre+) on Hyp phenotypes, A&B. Body weights (g) of male (left) and female (right) WT, WT/Hif1α(Cre+), Hyp, and Hyp/Hif1α(Cre+) mice were recorded every other week from weeks 4 through 12. (n ≥ 6 mice per group; *p < 0.01, #p < 0.05). C. Serum intact FGF23 was elevated in Hyp versus WT in the presence or absence of the Hif1α(Cre) allele. Female Hyp/Hif1α(Cre+) mice had slightly higher serum FGF23 compared with female Hyp. Bone structure in control and Hyp genetic crosses. Representative μCT images of distal femurs from 12 week old WT, WT/Hif1α(Cre+), Hyp, and Hyp/Hif1α(Cre+); D. male (left panel), E. female (right panel). Compared to genotype controls, Hyp mice had markedly widened distal femur (white arrows) consistent with their known ricketic phenotype, as well as far less trabecular bone.