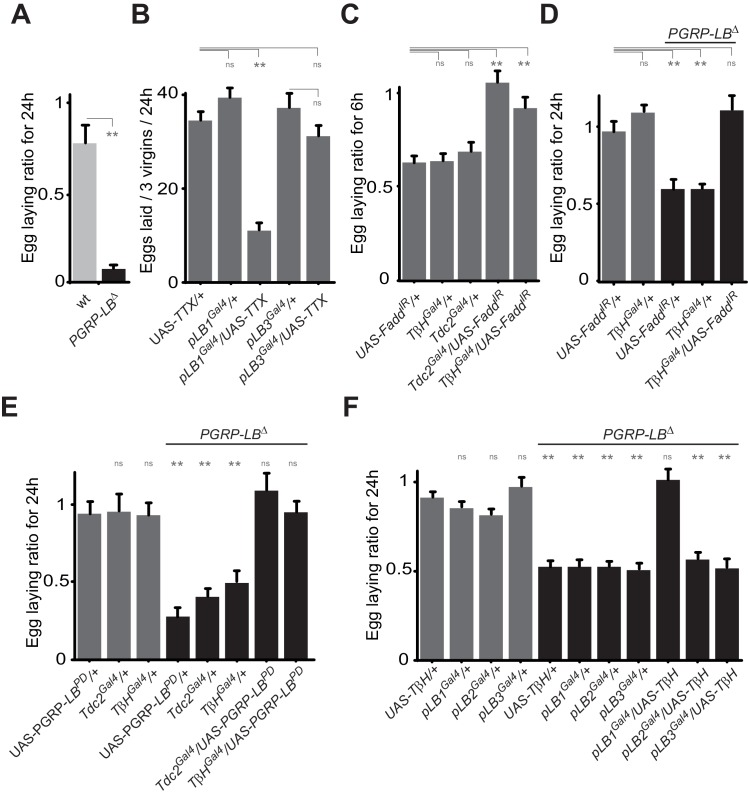
Figure 6. Bacteria modulate egg-laying behavior via the octopamine pathway.
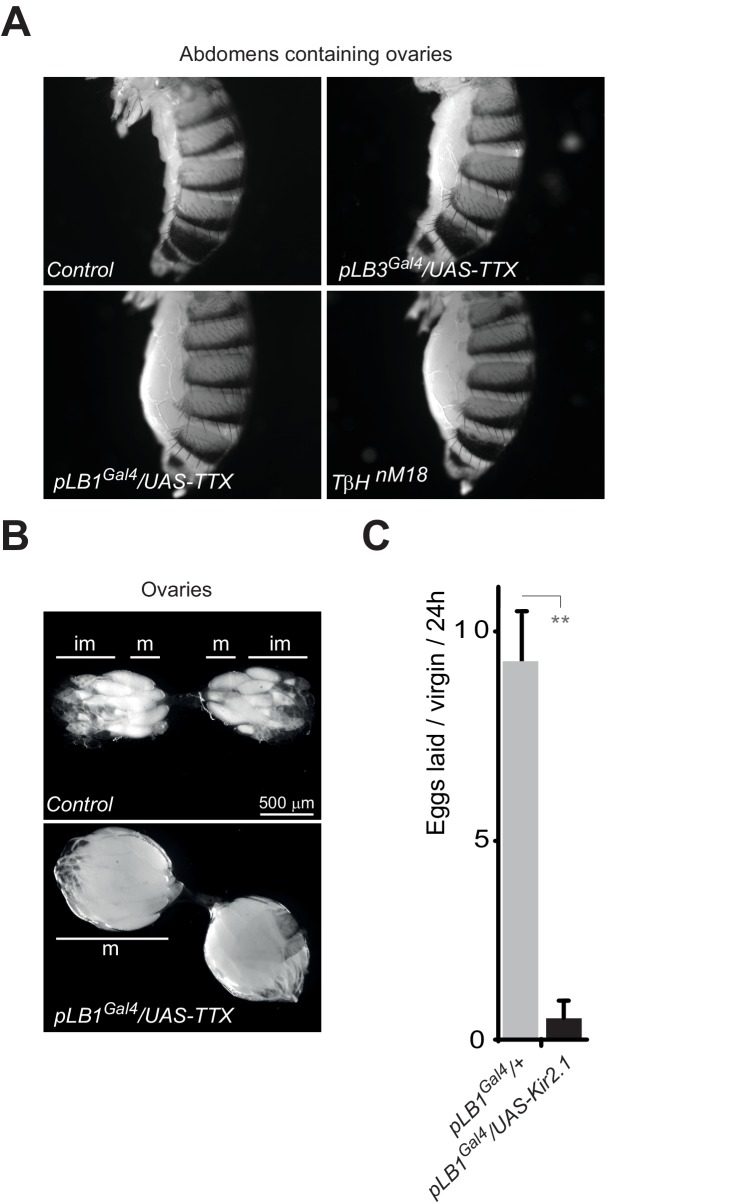
(A) Septic injury reduces egg laying in PGRP-LB virgin females. Egg-laying ratio post-septic injury of wt and PGRP-LB mutant virgin females. (B) Functional inactivation of pLB1, but not of pLB3-positive cells, by UAS-TTX blocks egg laying in virgin females. Total eggs laid by wild-type virgins in which the TTX is expressed in pLB1 or pLB3 cells. (C and D) Egg-laying ratio of wt (C) or PGRP-LB mutant mated females (D) in which the IMD pathway has been specifically inactivated via UAS-FaddIR ectopic expression in TβH or Tdc2-positive cells. (E) Restoring PGRP-LBPD expression in cells that produce the enzymes required to synthesize octopamine (tdc2 and TβH) fully rescues the PGRP-LB mutant phenotype following septic injury. Egg-laying ratio of PGRP-LB mutant females in which the tdc2 Gal4 and TβHGal4 drivers are used to overexpress the PGRP-LBPD isoform. (F) Providing an excess of TβH in pLB1 cells is sufficient to rescue PGRP-LB mutant phenotypes. Egg-laying ratio of PGRP-LB mutant mated females in which the TβH level has been increased in pLB1, pLB2 or pLB3 cells. For A, C, D, E and F; shown is the average egg-laying ratio ± SEM from at least two independent trials with at least 20 females per genotype and condition used. For (B); shown is the average number of eggs laid per three virgins per 24 hr ± SEM from at least two independent trials with at least 20 females per genotype and condition used. * indicates p<0.01; ** indicates p<0.001; n.s. indicates p>0.05, unpaired two-tailed Mann-Whitney test versus indicated controls for A, B, C and D and versus UAS in wt background for E and F.