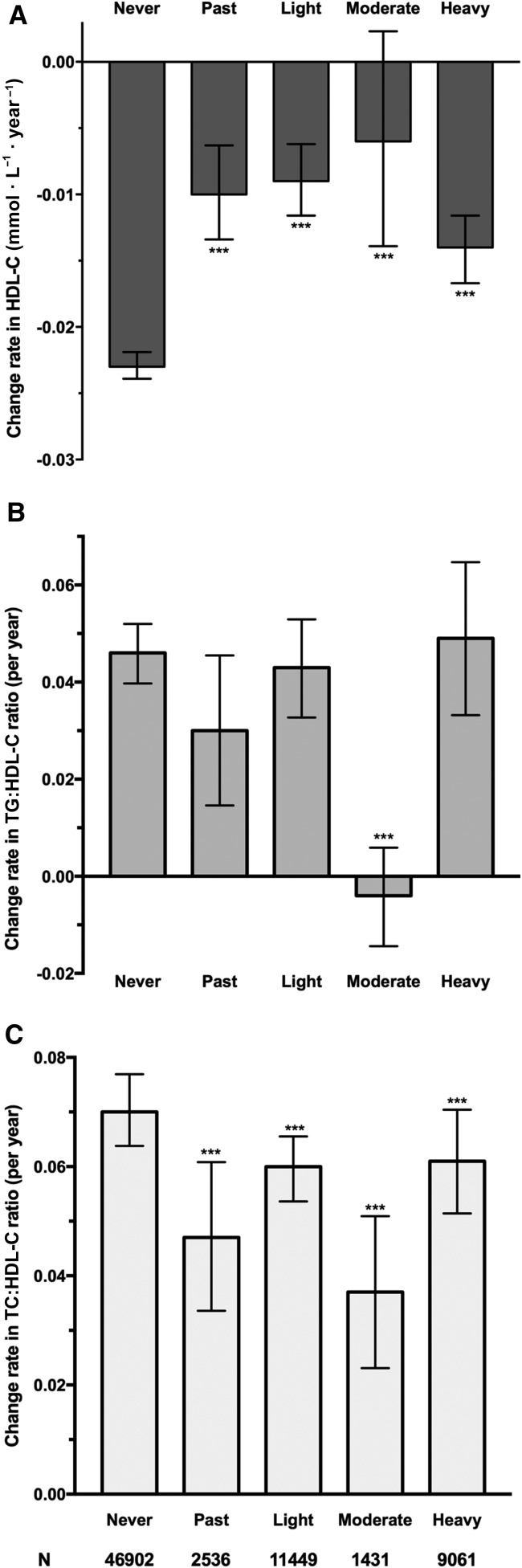
FIGURE 2.
Mean (95% CI) time-dependent change rates in HDL-C concentrations (mmol · L−1 · y−1) (A), the TC:HDL-C ratio (B), and the TG:HDL-C ratio (C) according to alcohol consumption. Models were adjusted for age, sex (men or women), physical activity (inactive, moderately active, or active), smoking status (never, past, occasionally, or daily), patients with diabetes (no, prediabetes, or yes), hypertension (no, prehypertension, or yes), BMI (in kg/m2; <24, 24–27.9, 28–29.9, or ≥30), waist circumference (<85 or ≥85 cm for women and <90 or ≥90 cm for men), C-reactive protein (<1, 1–2.9, or ≥3 mg/L), fatty liver (none, mild, or heavy), LDL cholesterol, and triglyceride. Participants were classified into the following categories of alcohol consumption: never, past, light (women: 0–0.4 servings/d; men: 0–0.9 servings/d), moderate (women: 0.5–1.0 servings/d; men: 1–2 servings/d), or heavy (women: >1.0 servings/d; men: >2 servings/d). Generalized estimating equation models were used to model the change rates and to test the differences in change rates compared with never drinkers. ***Compared with never drinkers, P < 0.001. HDL-C, HDL cholesterol; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride.