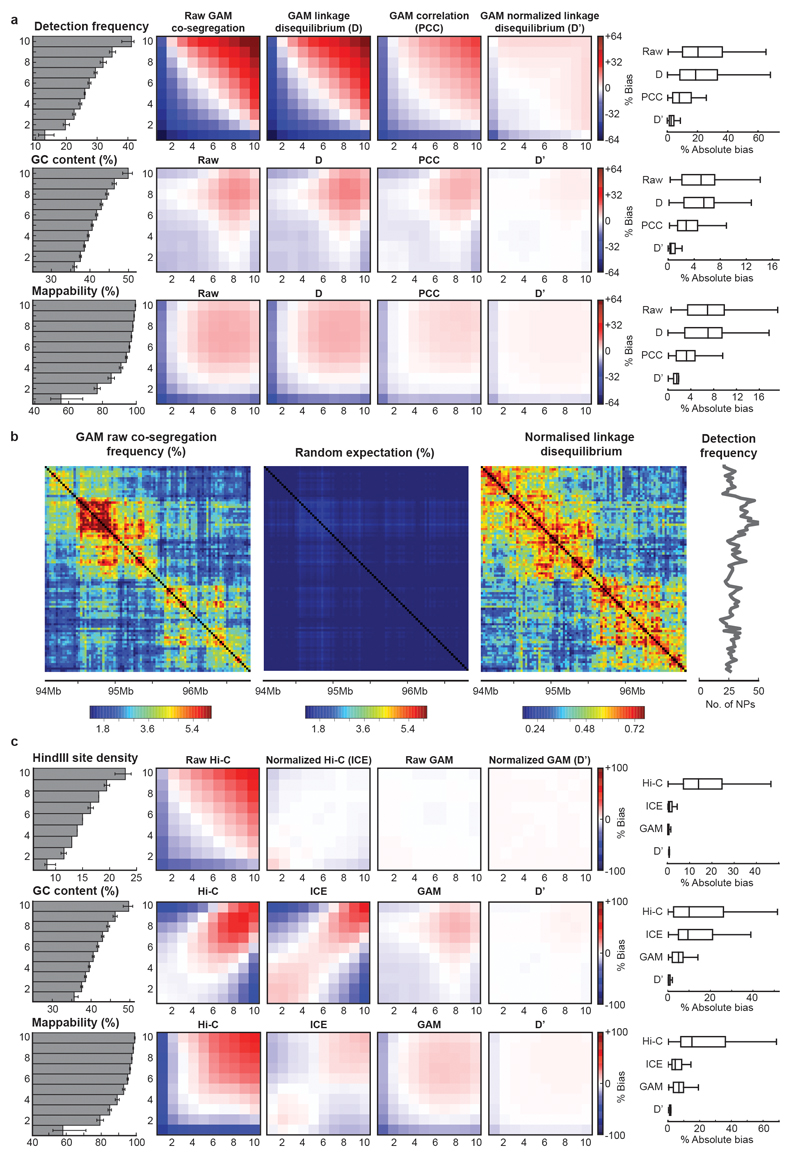
Extended Data Figure 4. Exploration and normalization of biases in the mESC-400 dataset.
a, Normalized linkage disequilibrium effectively reduces bias in GAM datasets. 30 kb windows were divided into equal groups according to their detection frequency, GC content or mappability (grey bar plots give mean ± interquartile range, left). Mean observed over expected values (% bias) between windows in each group are shown for three different normalization schemes (heat maps, middle). Calculating the normalized linkage disequilibrium results in the lowest absolute % bias in all three cases (box plots, right). b, The normalized linkage disequilibrium corrects for confounding effects on co-segregation matrices caused by small differences in the detection frequency of locus pairs. c, GAM matrices are less biased than Hi-C matrices both before and after ICE-normalization. Observed over expected values are given for 50 kb windows stratified by restriction site density, GC content and mappability.