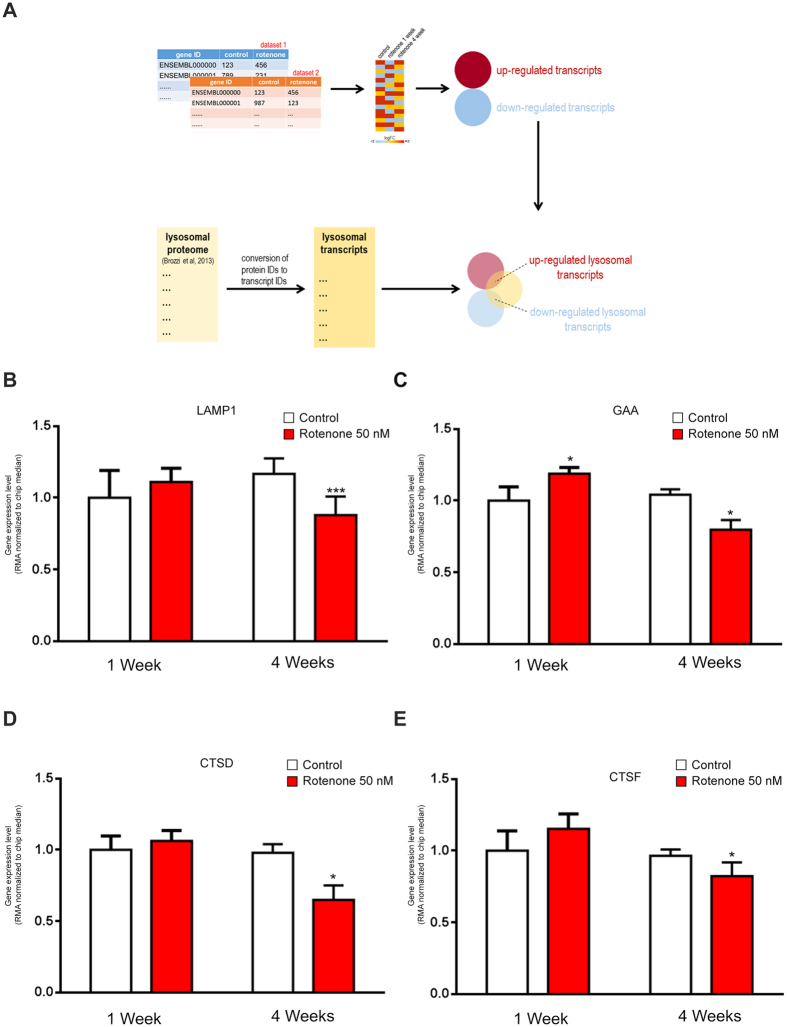
Figure 2. Effect of rotenone on lysosomal gene expression in SK-N-MC neuroblastoma cells.
(A) Illustration of the experimental strategy employed to determine lysosomal-related genes that are significantly affected by inhibition of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. (B) Relative transcript levels of LAMP1 in SK-N-MC neuroblastoma cells treated with the respiratory chain complex I inhibitor rotenone (50 nM) collected at 1 and 4 weeks of treatment, after RMA normalization. The white bar corresponds to the control MEFs and the red bars to the MEFs treated with rotenone with t test p-values indicated (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.001). (C) Relative transcript levels of GAA in SK-N-MC neuroblastoma cells treated with the respiratory chain complex I inhibitor rotenone (50 nM) collected at 1 and 4 weeks of treatment, after RMA normalization. The white bar corresponds to the control MEFs and the red bars to the MEFs treated with rotenone with t test p-values indicated (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.001). (D) Relative transcript levels of CTSD in SK-N-MC neuroblastoma cells treated with the respiratory chain complex I inhibitor rotenone (50 nM) collected at 1 and 4 weeks of treatment, after RMA normalization. The white bar corresponds to the control MEFs and the red bars to the MEFs treated with rotenone with t test p-values indicated (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.001). (F) Relative transcript levels of CTSF in SK-N-MC neuroblastoma cells treated with the respiratory chain complex I inhibitor rotenone (50 nM) collected at 1 and 4 weeks of treatment, after RMA normalization. The white bar corresponds to the control MEFs and the red bars to the MEFs treated with rotenone with t test p-values indicated (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.001).