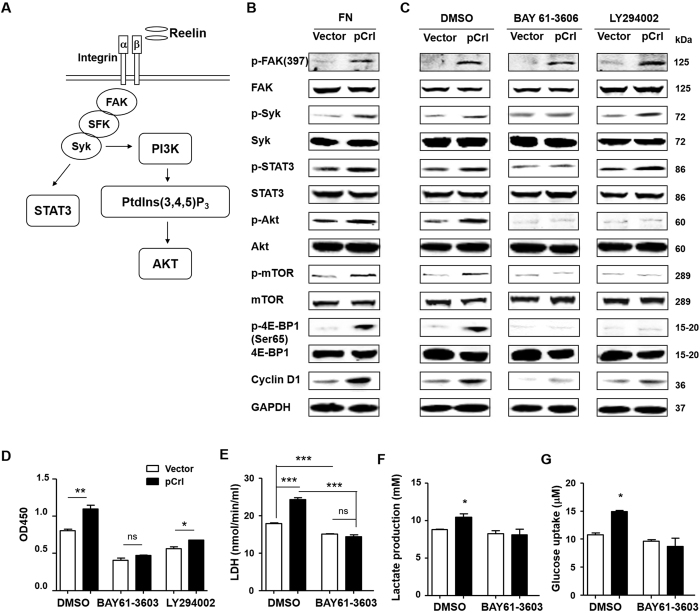
Figure 5. Reelin promotes MM cell growth and glycolysis via Syk/Akt pathway.
(A) Diagram of Reelin-induced signaling pathways in MM cells. (B) Reelin induces the activation of Syk and Akt/mTOR pathways. H929 cells were transfected with pCrl or vector for 40 hours. The cells were then seeded in FN-coated plates. One hour later, the cells were harvested and cell lysates were subjected to western blotting with phospho-FAK (Tyr397), FAK, phospho-STAT3 (Tyr705), STAT3, phospho-Syk (Tyr525/526), Syk, phospho-Akt (Ser473), Akt, phospho-mTOR (Ser2448), mTOR, phospho-4E-BP1 (Ser65), 4E-BP1, and Cyclin D1-specific antibodies. An antibody specific for GAPDH was used as the loading control. (C,D) The suppression effect of Syk and PI3K inhibitors on Reelin-mediated cell growth. H929 cells were transfected with pCrl or control plasmid and were then cultured in FN-coated plates. The cells were treated with DMSO, Syk inhibitor BAY 61–3606, or PI3K inhibitor LY 294002 for 24 hours. A fraction of the cells were lysed and subjected to western blotting (C) and the rest were measured by CCK8 method (D). (E–G) Syk is involved in Reelin-induced glycolysis. H929 cells were transfected with pCrl or vector for 40 hours. The cells were then cultured in FN-coated plates and were treated with DMSO or Syk inhibitor BAY 61-3606 for 24 hours. The levels of LDH (E), L-Lactate (F) and glucose uptake (G) of the cells were then measured. The results are representative of two to three independent experiments.