Figure 6. Therapeutic efficacy of ML385 as a single agent and in combination with carboplatin in subcutaneous lung tumor xenografts.
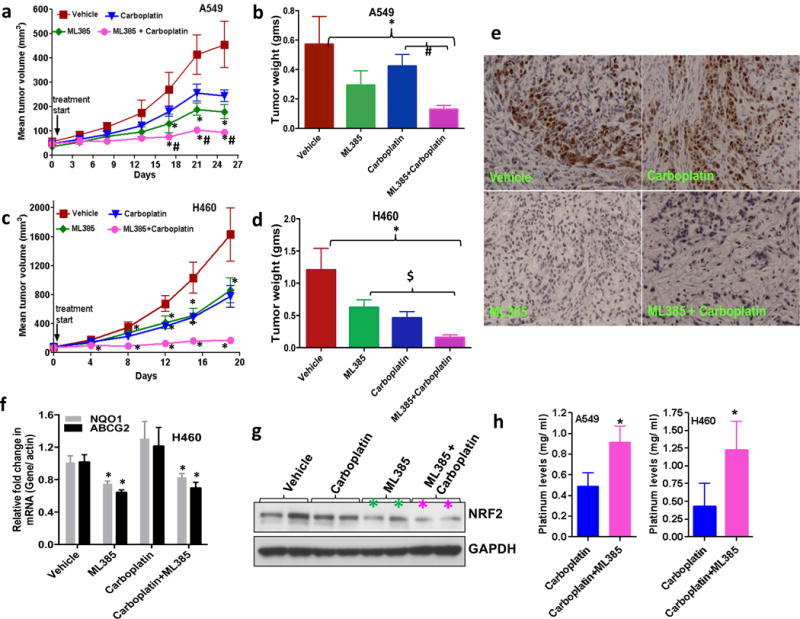
(a) ML385 shows anti-tumor activity as a single agent in sensitized A549 xenograft tumors to carboplatin therapy. Values represent tumor volume ± S.E.M. for all groups. n = 7 mice/group; ‘*’P<0.05 relative to vehicle; ‘#’ P<0.05 relative to carboplatin. (b) Treatment with ML385 or ML385 in combination with carboplatin significantly reduced tumor weight as compared to vehicle group. Efficacy of ML385 alone was comparable to carboplatin. ‘*’P<0.05 relative to vehicle; ‘#’ P<0.05 relative to carboplatin. (c-d) ML385 sensitized H460 lung tumors to carboplatin treatment. Groups of H460 tumors treated with ML385 or ML385 in combination with carboplatin showed a significant reduction in tumor volume and weight as compared to the vehicle group. Efficacy of ML385 alone was comparable to carboplatin. n = 5–7 mice/group; ‘*’P<0.05 relative to vehicle; ‘$’ P<0.05 relative to ML385. (e) The proliferative index based on Ki-67 immuno-reactivity in A549 subcutaneous tumors. (f) Treatment with ML385 attenuated the expression of NRF2-dependent genes in H460 tumors. ‘*’P<0.05 relative to vehicle or carboplatin (g) Immunoblot showing reduction in NRF2 protein in H460 tumors treated with ML385. (h) Bar graph showing platinum levels in A549 and H460 tumors treated with carboplatin alone or ML385 in combination with carboplatin. ‘*’P<0.05, relative to carboplatin alone.
