Figure 3.
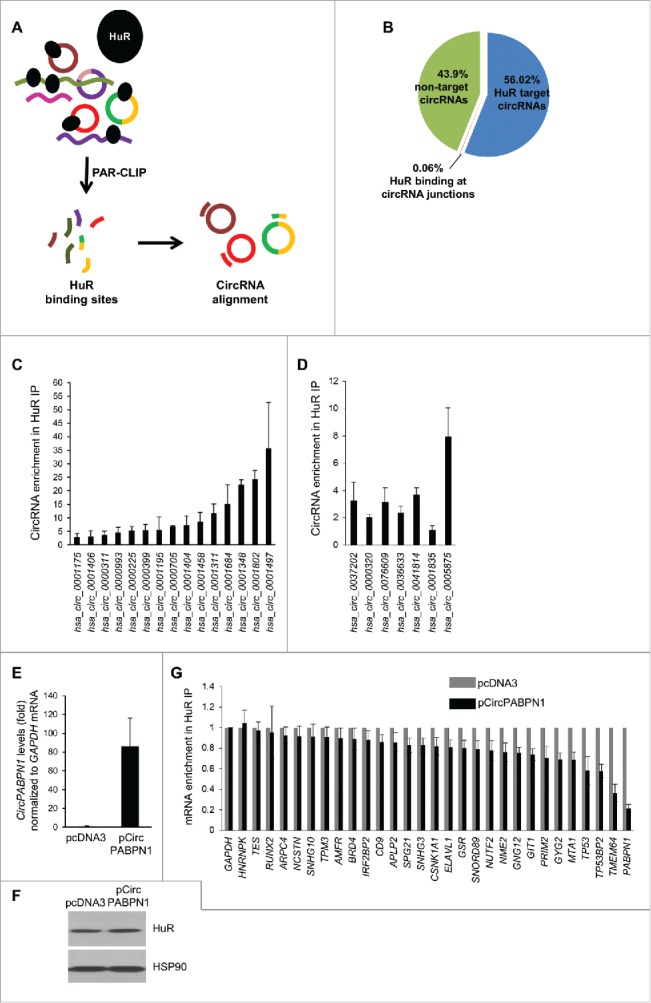
Transcriptome-wide identification and validation of HuR target circRNAs. (A) Schematic representation of the strategy used to identify globally HuR-interacting circRNAs using publicly available CLIP data sets (Methods). (B) Among the annotated circRNAs (CircBase, Aug 4 2015), ∼56% potentially contained HuR target sites, 44% did not, and for <1% HuR binding sites were at the junction. Among the putative target, most HuR binding sites were found within the body, and a few spanned the junction. (C, D) Partial validation of HuR target circRNAs found in panel (B) by RIP (HuR IP relative to IgG IP) followed by RT-qPCR analysis; circRNAs with HuR sites in the body (C) and the junction (D) were studied. (E-G) HeLa cells were transfected with either pcDNA3 or with pCircPABPN1; 48 h later, the levels of CircPABPN1 were assessed by RT-qPCR analysis (normalized to GAPDH mRNA) (E), the levels of HuR by Western blot analysis (loading control HSP90) (F), and the interaction of HuR with target mRNAs by RIP followed by RT-qPCR analysis (normalized to GAPDH mRNA) (G). Data in (C-E,G) represent the means ± SEM from three independent experiments; data in (F) are representative of three repeats.
