Figure 1.
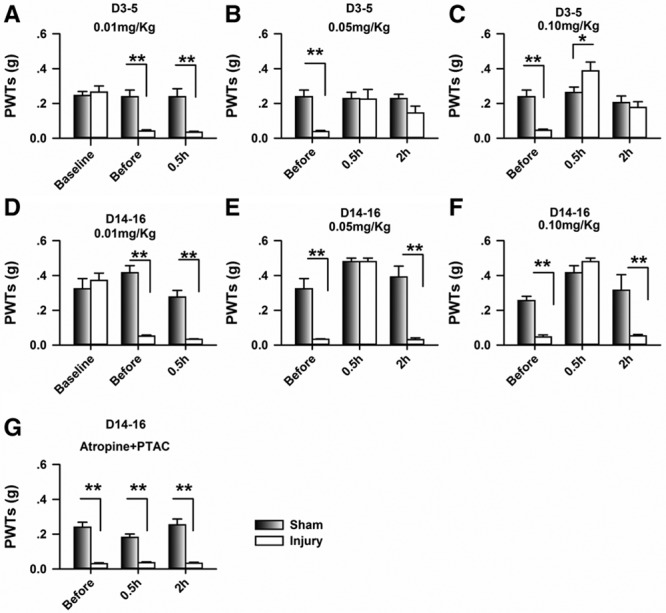
Application of (5R,6R)6-(3-propylthio-1,2,5-thiadiazol-4-yl)-1-azabicyclo[3.2.1] octane (PTAC) systemically raised the paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) in nerve-injured mice. A, Nerve injury decreased the PWT, which was not changed by the application of PTAC at 0.01 mg/kg at day 3 after nerve injury (2-way RM ANOVA, sham versus injury: F1;44 = 17.46, P < .01; treatments: F2;44 = 16.78, P < .01, interaction: F2;44 = 14.98, P < .01, n = 7 for sham, n = 8 for injury group, **P < .01 under SNK test). B, PTAC at 0.05 mg/kg increased the PWTs of the nerve-injury groups injected at day 4 after nerve injury (2-way RM ANOVA, sham versus injury: F1;44 = 9.32, P < .01; treatments: F2;44 = 2.98, P = .07, interaction: F2;44 = 3.79, P < .05, n = 7 for sham, n = 8 for injury group, **P < .01 under SNK test). C, PTAC at 0.05 mg/kg increased the PWTs of the nerve-injury groups injected at day 5 after nerve injury (2-way RM ANOVA, sham versus injury: F1; 44 = 0.98, P = .34; treatments: F2;44 = 16.63, P < .01, interaction: F2; 44 = 11.76, P < .01, n = 7 for sham, n = 8 for injury group, * P < .05, **P < .01 under SNK test). D, PTAC at 0.01 mg/kg had no effect on the PWTs in the sham and nerve-injury groups injected at day 14 after nerve injury (2-way RM ANOVA, sham versus injury: F1;29 = 32.95, P < .01; treatments: F2;29 = 14.71, P < .01, interaction: F2;44 = 17.49, P < .01, n = 5 for each group, **P < .01 under SNK test). E, PTAC at 0.05 mg/kg increased the PWTs of the nerve-injury groups injected at day 15 after nerve injury (2-way RM ANOVA, sham versus injury: F1;29 = 69.17, P < .01; treatments: F2;29 = 35.73, P < .01, interaction: F2;29 = 11.94, P < .01, n = 5 for each group, **P < .01 under SNK test). F, PTAC at 0.10 mg/kg increased the PWTs in both the sham and nerve-injury group injected at day 16 after nerve injury (2-way RM ANOVA, sham versus injury: F1;29 = 12.54, P < .01; treatments: F2;29 = 33.56, P < .01, interaction: F2;29 = 9.76, P < .01, n = 5 for each group, *P < .05, **P < .01 under SNK test). G, The application of atropine (i.p., 0.1 mg/kg) blocked the analgesic effects of PTAC (0.10 mg/kg) (2-way RM ANOVA, sham versus injury: F1;56 = 260.17, P < .01; treatments: F2;56 = 1.52, P = .23, interaction: F2;56 = 1.93, P = .16; n = 10 for sham, n = 9 for injury group, **P < .01 under SNK test). ANOVA indicates analysis of variance; RM, repeated measures; SNK, Student-Newman-Keuls.
