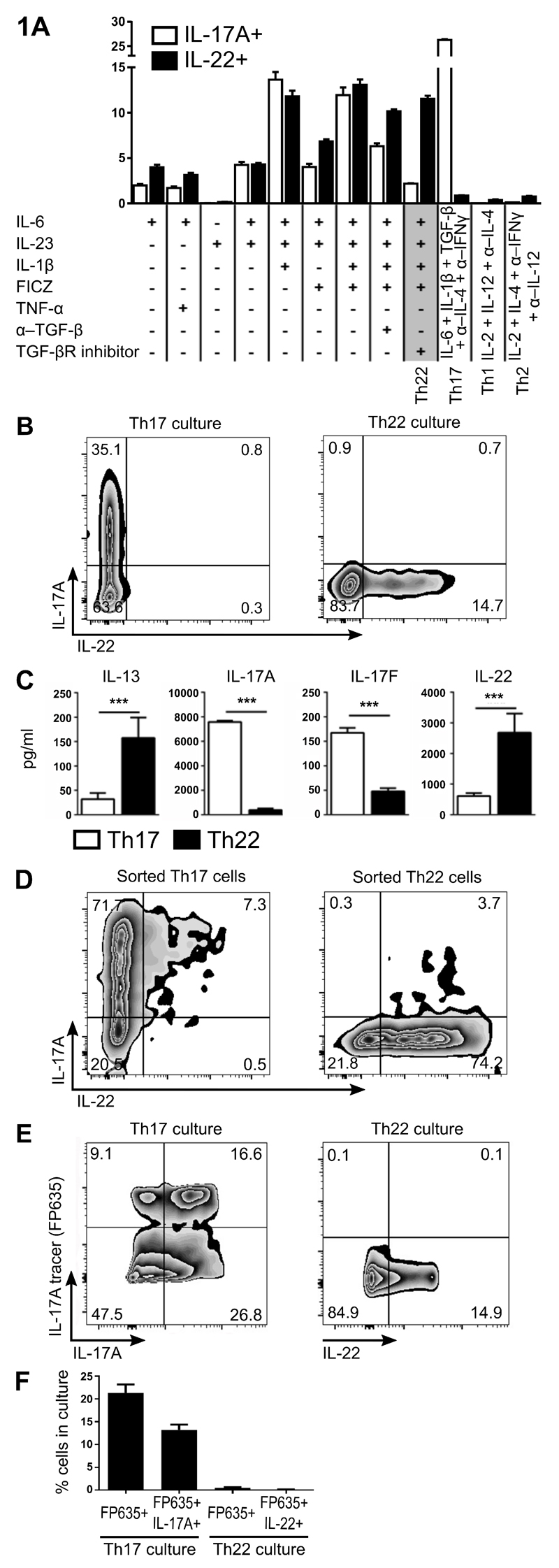
Figure 1. Generation of Th22 cells that appears to be a distinct lineage to Th17 cells.
Determination of optimal culture conditions for Th22 cells (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-23, FICZ and TGF-βR inhibitor/Galunisertib, with anti-IL-4/IFNγ). Percentage of IL-17A+ and IL-22+ cells after culturing naïve Th cells under various polarizing conditions are graphed (A). Representative plots of naïve Th cells stimulated for 3 d under optimal Th17 conditions or Th22 conditions (B). Cytokine protein levels in culture SN from naïve Th cells stimulated for 3 d under optimal Th17 conditions or Th22 conditions (C). Naïve Th cells from IL-17eGFP x IL-22tdTomato reporter mice were differentiated with Th17 or Th22 conditions then FACS sorted to purify Th17 or Th22, respectively. Representative plots of FACS-sorted Th17 and Th22 cells re-stimulated for 3 d under Th0 conditions (D). Representative plots (E), and percentage quantitation (F) of IL-17A fate mapping reporter (IL-17A tracer: Il17aFP635) expression versus IL-17A or IL-22 protein expression in naïve Th cells differentiated for 3 d under optimal Th17 or Th22 conditions. Cell populations in FACS plots are pre-gated on CD4+CD44+ and viable cells. Error bars represent SEM (n=6 per group from three independent experiments). ***p<0.001.