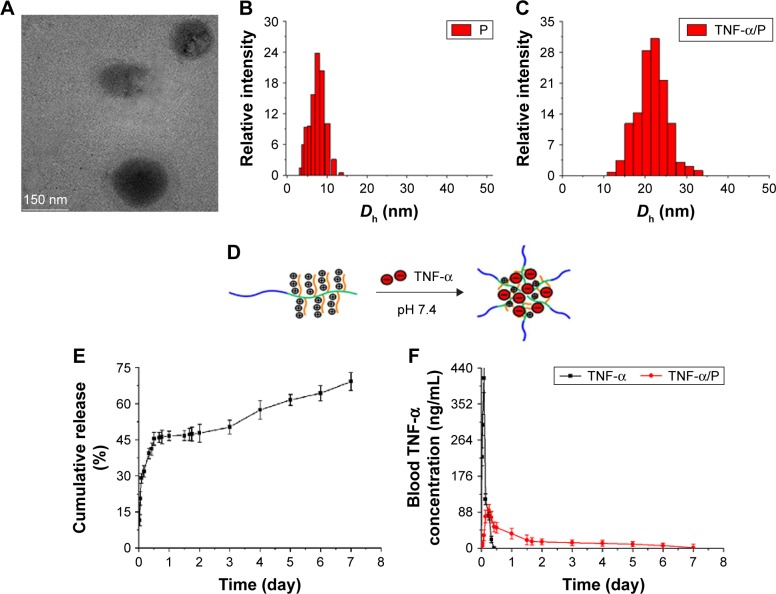
Figure 2.
Characterization of PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL) and TNF-α/PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL) complexes.
Notes: (A) TEM image of TNF-α/PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL) complexes. (B) The hydrodynamic diameter (Dh) of block copolymer PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL). (C) The hydrodynamic diameter (Dh) of TNF-α/PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL) complexes. The mean diameter of polymer and TNF-α/polymer was ~7 nm and ~26 nm. (D) Encapsulation of TNF-α by the block copolymer PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL). (E) Cumulative release profile of TNF-α from TNF-α/PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL) complexes (n=5). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. TNF-α was released in a sustained manner from the nanocarrier over 7 days. (F) Blood TNF-α concentration after injection of TNF-α and TNF-α/PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL) complexes in rats (n=5). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Parameters: 415.3 ng/mL (Cmax), 2 h (Tmax), and 10 h (baseline) for TNF-α group; and 92.34 ng/mL (Cmax), 6 h (Tmax), and 7 days (baseline) for TNF-α/P group. The release of TNF-α in the TNF-α/P group was substantially sustained compared with that in TNF-α group.
Abbreviations: TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; P, polymer; PEG-b-(PELG-g-PLL), poly(ethylene glycol)-b-(poly(ethylenediamine L-glutamate)-g-poly(L-lysine)); TEM, transmission electron microscopy; SD, standard deviation.