Figure 1.
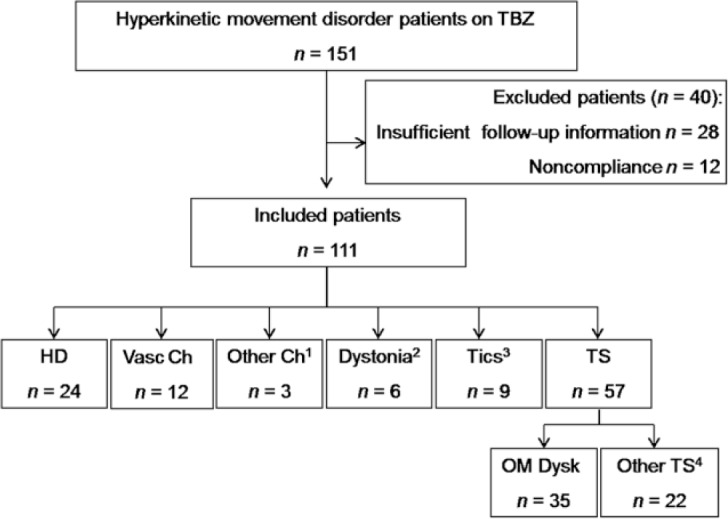
Patient selection.
(1) Including: neurolupus (n = 1), striatum cavernous angioma (n = 1), and hyperthyroidism (n = 1).
(2) Including: generalized hereditary dystonia (SCA3, n = 1), generalized acquired dystonia (iatrogenic, n = 1, viral encephalitis, n = 1, perinatal encephalopathy, n = 1), and segmental idiopathic sporadic (n = 2).
(3) Including: Gilles de la Tourette syndrome (n = 3, with simple motor and vocal tics) and chronic tic disorder (n = 6, with simple motor tics, and combined simple and complex motor tics).
(4) Including: dystonia (n = 9), chorea (n = 4), akathisia (n = 1), tics (n = 1) and OM plus (+ chorea, tics or dystonia, n = 7).
TBZ, tetrabenazine; HD, Huntington disease; Vasc, vascular; Ch, chorea; TS, tardive syndrome; OM Dysk, oromandibular dyskinesia; SCA3, Spinocerebellar ataxia type 3.
