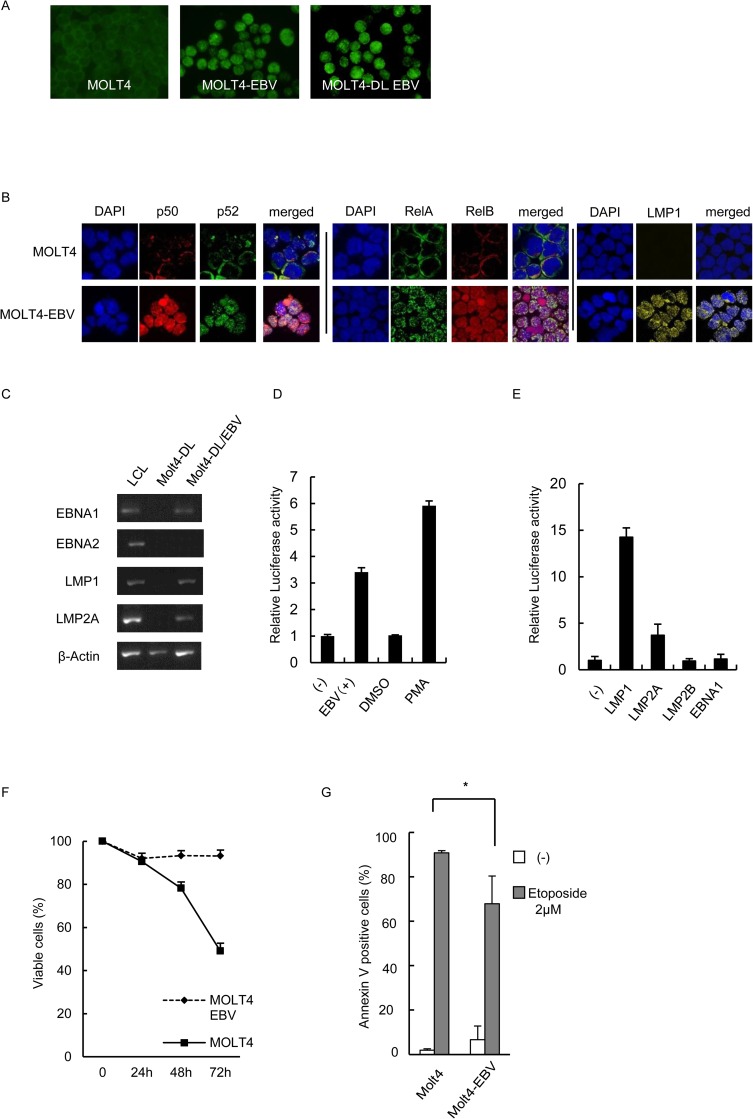
Fig 3. The effects of Epstein-Barr virus infection on MOLT4 cells.
(A) The original (left), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected MOLT4 (middle), and EBV-infected MOLT4-DL cells (right) were obtained for EBNA1 staining. Green fluorescent cells are EBNA1-positive. (B) Immunofluorescent staining for NF-κB protein localization in EBV-infected MOLT4 cells (MOLT4-EBV). The original and MOLT4-EBV cells were subjected to immunofluorescent staining with anti-p50, p52, RelA, and RelB antibodies as indicated. DAPI was used for nuclear staining. Cells were analyzed via confocal microscopy. (C) Reverse-transcriptase PCR analysis of EBV protein-encoding gene expression in EBV-infected MOLT4-DL cells. Infection was confirmed via detection of mRNAs encoding the viral proteins EBNA1, LMP1, LMP2A, and LMP2B. EBNA2 expression was not detected, and the infection type was considered latency type 2. (D) Dual luciferase assay for NF-κB in EBV-infected MOLT4-DL cells. As a positive control, MOLT4-DL cells were treated with 20 nM phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) for 18 h. (E) Luciferase reporter gene assay using expression vectors for EBV proteins in MOLT4 cells. MOLT4 cells were transfected with 10 μg of EBNA1, LMP1, LMP2A, LMP2B, or empty vector as indicated, along with 10 μg of pNF-κB-luc and 1 μg of pRLSV40. Twelve hours after transfection, cells were harvested for the dual luciferase assay. Luciferase activity was normalized to Renilla luciferase activity and expressed as an increase relative to the control. Data are shown as the means ± standard deviations of 3 independent experiments. (F) The original and EBV-infected MOLT4 cells were cultured in 10% FCS–RPMI or FCS-free RPMI. The time-dependent viable cell numbers were examined by trypan-blue staining. Data are shown as the means ± standard deviations of 3 independent experiments. (G) The original and EBV-infected MOLT4 cells were cultured for 24 h in 10% FCS–RPMI with or without 2 μM VP16. The viable and apoptotic cell numbers were then determined by Annexin V staining, and the percentage of Annexin V-positive cells was determined. * p = 0.03245. Each experiment was independently performed 3 times, and the average data are presented.