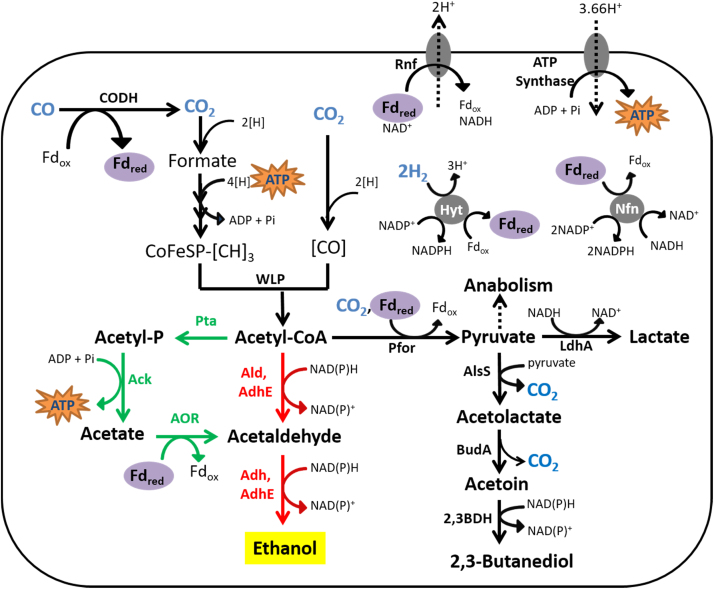
Fig. 1.
Autotrophic product formation in C. autoethanogenum. The ATP-efficient, indirect ethanol route employing phosphotransacetylase (Pta), acetate kinase (Ack) and aldehyde:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (AOR) are depicted in green. The direct ethanol biosynthesis route utilizing bi-functional aldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase (AdhE), CoA-dependent acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (Ald) and alcohol dehydrogenase (Adh) is shown in red. AlsS = acetolactate synthase; 2,3-BDH =2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase; BudA = acetolactate decarboxylase; CODH = carbon monoxide dehydrogenase; CoFeSP = corrinoid iron sulphur protein; Fdox = oxidized ferredoxin; Fdred = reduced ferredoxin; Hyt = NADP-dependent electron bifurcating hydrogenase; LdhA = lactate dehydrogenase; Nfn = transhydrogenase; Pfor = pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase; Rnf = H+-translocating ferredoxin: NAD+-oxidoreductase; WLP = Wood-Ljungdahl Pathway. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)