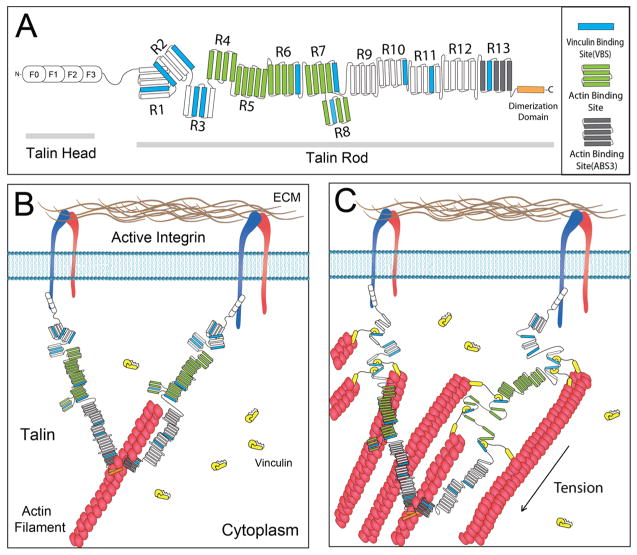
Figure 4.
Schematics of talin structure and interaction of talin dimer with vinculin in cell. (A) Illustration of domain structure of full-length talin. Talin head domain contains a FERM domain (50 kDa), followed by a flexible “neck”(10 kDa), which connects the head domain to its C-terminal rod domain (220 kDa). The rod domain contains 11 cryptic VBS (drawn in blue). The dimerization domain is a single helix that sits at the end of the rod domain. (B) In the initial stage of FA formation, talin dimer binds to actin and integrin. At this stage, the cryptic VBSs remain buried among the α-helical bundles. (C) As the actin filament starts to pull on talin, the former buried VBS starts to reveal to allow vinculin binding, and subsequently more actin filament recruitment.