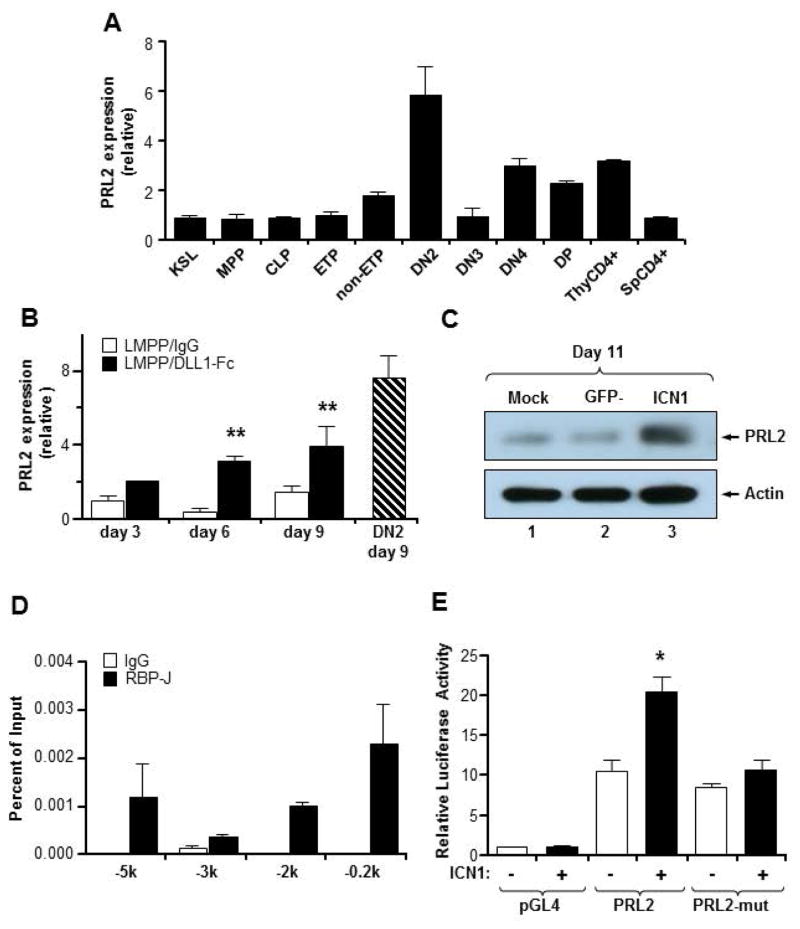
Figure 4. Notch signaling regulates PRL2 expression during T cell differentiation.
(A) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of PRL2 expression in sorted MPPs, CLPs, ETPs, DN2, DN3, DN4, DP, and CD4+ thymocytes, presented relative to expression in KSLs, set as 1. PRL2 is highly expressed in DN2 cells. n = three biological replicates. (B) Sorted Prl2+/+ LMPPs were cultured in the presence or the absence of DLL1-Fc. Cells were collected at each time point and PRL2 expression was determined by quantitative real-time PCR analysis. **P<0.01, n = three biological replicates. (C) Notch-ICN1 was introduced into Prl2+/+ Lin−Sca1+ cells and the levels of PRL2 protein were determined by western blot analysis. (D) Chromatin-bound DNAs from Tail-7 cells were immunoprecipitated with a RBPJ-antibody or normal mouse IgG. Quantitative real-time PCR amplification was performed on corresponding templates using primers for PRL2 gene. (E) Notch-ICN1 transactivates PRL2 promoter. 293 cells were transfected with PRL2 promoter driven luciferase reporter plasmids containing either RBPJ binding sites or mutant RBPJ binding sites. Luciferase activity was assayed 24 hours after transfection. *P<0.05, n=3.