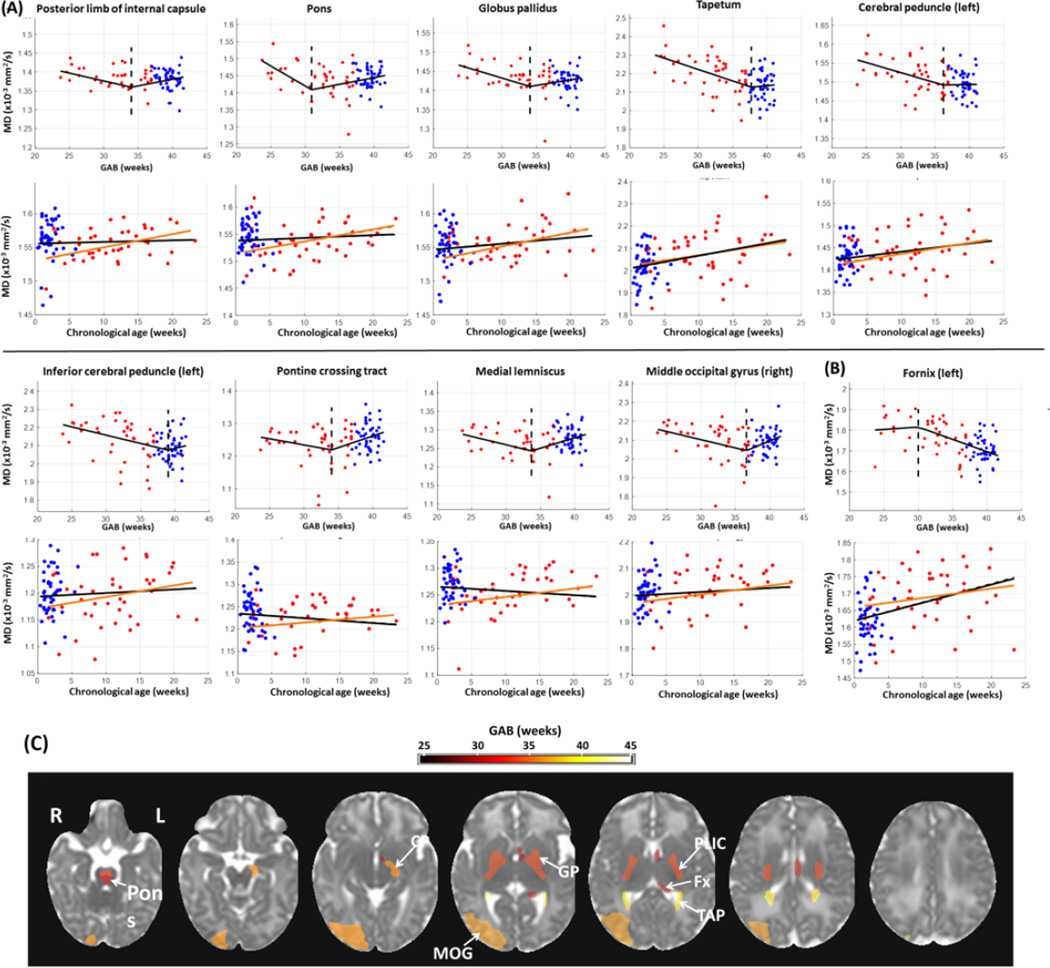
Figure 2.
Change point analysis of MD measurements (corrected for PMA at scan and gender) in the structures with significant change points (familywise p<0.05). (A–B) First row for each structure: change of MD against GAB, after correcting for PMA at scan and gender. The red and blue dots denote data from preterm and term-born neonates, respectively. The black lines show FA values fitted to GAB only, and dashed lines indicate the change points. Second row for each structure: change of MD against chronological age, after correcting for PMA at scan and gender. The black lines indicated the linear regression between FA and chronological age with both the term and preterm-born infants, and the orange lines showed the linear fitting with only the preterm data. For the structures that were bilaterally significant, only one side (left side) was presented; for those that were significant only in one side, the laterality is indicated in the plots. In a majority of regions (n=15), MD decreased with GAB before the change point, and remained relatively stable after the change point (A). Conversely, MD values in left fornix (B) were relatively stable before the change point and then decreased with GAB after the change point. (C): Change point values of MD in regions with significant change points (family-wise p<0.05), overlaid on the JHU neonate MD atlas. The color bar indicates change points in units of GAB (weeks). Abbreviations: CP –cerebral peduncle; MOG –middle occipital lobe; GP –globus pallidus; PLIC –posterior limb of internal capsule; Fx –fornix; TAP –tapetum.