Figure 3.
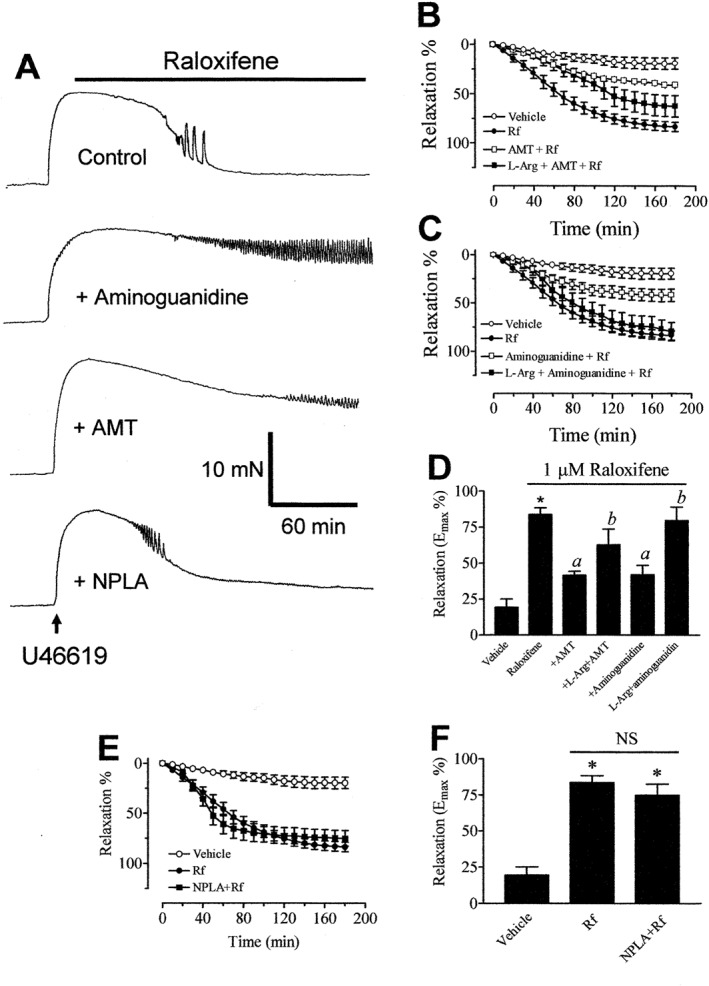
(A) Recordings showing the time course of raloxifene‐induced relaxation in endothelium‐denuded aortic rings in control and in the presence of 100 μM AMT‐HCl or 100 μM aminoguanidine. Inhibitory effect of AMT‐HCl (B) or aminoguanidine (C) on raloxifene (1 μM)‐induced aortic relaxation. (D) The maximal relaxant effect of raloxifene in the absence and presence of iNOS inhibitors. (E) Treatment with NPLA (100 μM) was without effect on raloxifene‐induced relaxation. (F) The maximal relaxant effect of raloxifene in the absence and presence of NPLA. Statistical differences are indicated by * (P < 0.05) between vehicle control and raloxifene group, a (P < 0.05) between raloxifene and other treatment groups and b (P < 0.05) between AMT‐HCl/aminoguanidine and treatment groups. Results are mean ± SEM of 6–11 rings from different rats.
