Figure 6.
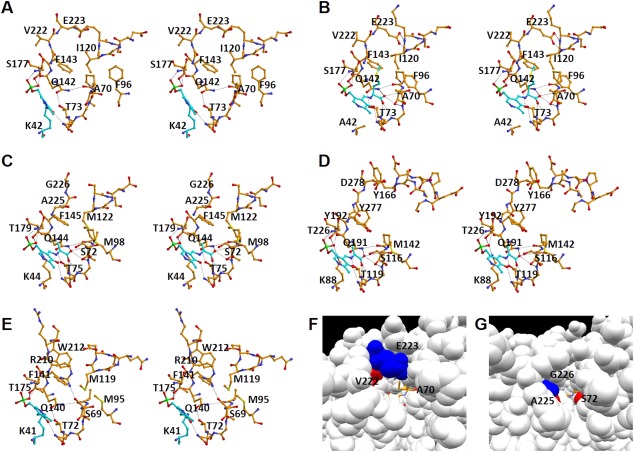
Active site structure. A: Active site of the wild‐type L. plantarum CBS in the open form in which the internal aldimine is formed. B: Active site of the K42A variant of the L. plantarum CBS in the closed form bound to the external aldimine. C: Active site of the M. tuberculosis OASS‐A in the closed form bound to the α‐aminoacrylate intermediate.28 D: Active site of the Drosophila CBS in the closed form bound to the α‐aminoacrylate intermediate.29 E: Active site of the E. coli OASS‐B in the closed form in which the internal aldimine is formed.33 Carbon atoms of PLP and the PLP‐attached residue (Lys residue in A and E) or PLP‐attached compounds (l‐methionine in B and α‐aminoacrylate in C and D) are shown in light sky blue. F: Substrate‐binding pocket of the L. plantarum CBS in the closed form. G: Substrate‐binding pocket of the M. tuberculosis OASS‐A in the closed form. In F & G, key amino acid residues are colored red or blue. External aldimine was shown in the stick model colored in orange.
