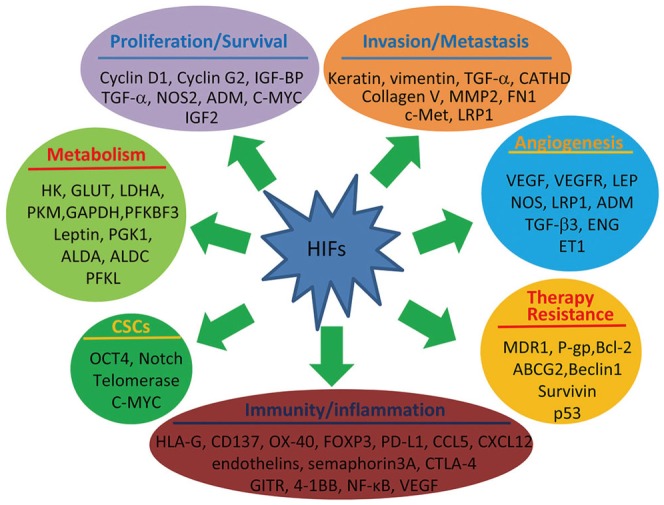
Fig. 2. Representative HIF-targeted genes and their roles in cancer progression and therapy resistance. ALDA, aldolase A; ALDC, aldolase C; ADM, adrenomedullin; ABCG2, ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 2; CATHD, cathepsin D; CCL, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; ENG, endoglin; ET1, endothelin-1; FN1, fibronectin 1; FOXP3, forkhead box P3; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-P-dehydrogenase; GITR, glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein; GLUT, glucose transporter; HK, hexokinase; HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; HLA-G, human leukocyte antigen G; IGF2, insulin-like growth factor 2; IGF-BP, insulin-like growth factor binding protein; LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase A; LRP1, LDL-receptor-related protein 1; MDR1, multidrug resistance 1; MMP2, matrix metal-loproteinase 2; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NOS2, nitric oxide synthase 2; OCT4, octamer-binding transcription factor 4; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; PFKBF3, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase-3; PFKL, 6-phosphofructokinase, liver type; PGK1, phosphoglycerate kinase 1; PKM, pyruvate kinase M; TGF, transforming growth factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, VEGF receptor.