Figure 9.
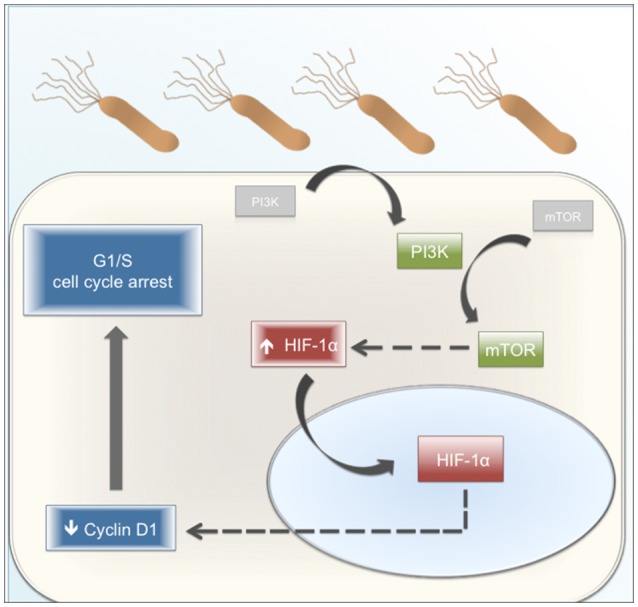
Proposed working model. H. pylori infection promotes the activation of PI3K and subsequently, of mTOR. The activation of this pathway increases the levels of HIF-1α, a protein mainly present in the nucleus. H. pylori-induced HIF-1α decreases the Cyclin D1 levels by a post-translational mechanism. Cyclin D1 is a protein necessary for G1 phase progression. Therefore, its reduction affects the normal progression of the cell cycle, promoting an arrest in G1 phase. Gray boxes: Inactive protein kinases. Green boxes: Active protein kinases associated with cell cycle progression. Blue boxes: effects linked to cell cycle arrest. Red boxes: HIF-1α as a switch between cell cycle progression and cell cycle arrest. Dashed arrows: steps ocurring by mechanism(s) that were not defined in this study.
