Fig. 7.
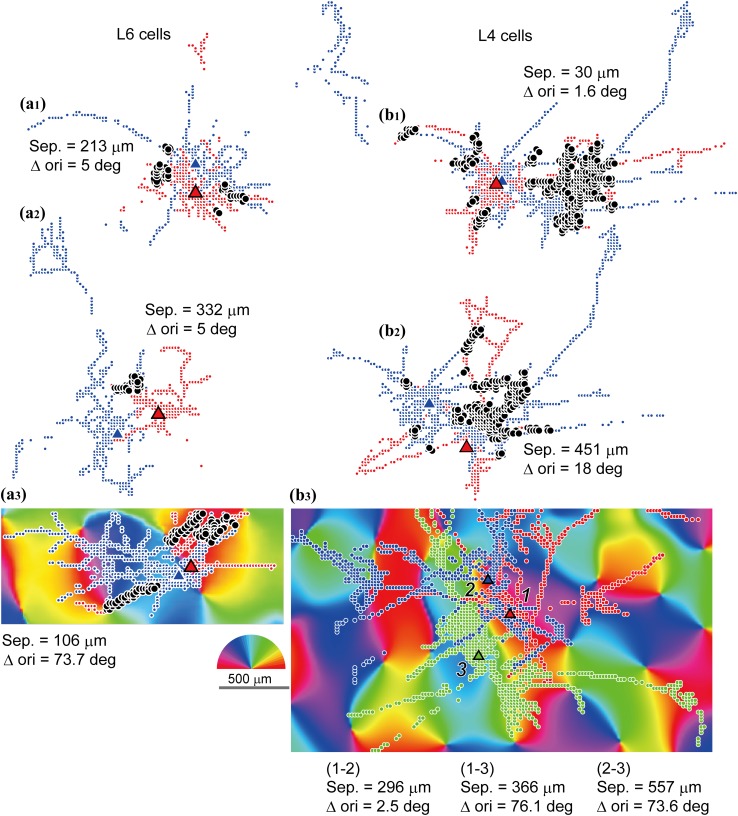
Examples for spatial overlap between boutons of pairs of L6 and L4 spiny cells. a 1, a 2 Boutons (red and blue dots) and somata (triangles of the same color as the boutons) of nearby L6 neuron pairs possessing similar orientation preference. The bouton distributions of neighboring cells show spatial overlap at just the same image pixel (black dots). As shown in Figs. 8 and 9, overlapping pixel positions are shown only for distal boutons defined as >250 μm away from the parent soma. a 3 Boutons (red and blue dots) and somata (triangles) of two neighboring L6 cells are superposed on orientation map. Although the cell bodies are located at different orientation preference domains bouton overlap is still observable (black dots). b 1, b 2 Pairwise comparison of neighboring L4 cells possessing similar orientation preference with each other. The axons are elongated chiefly toward similar directions and the distal boutons overlap to a large extent (black dots). b 3 Three neighboring L4 cells. Somata of cells 1 and 2 occupy similar orientations (red and blue triangles), whereas soma of cell 3 has a different orientation preference (green triangle). Cell 1 and 2 shows a relatively high bouton overlap with each other, whereas cell 3 has only a small overlap with the others, although soma separation between cell 3 and 1 is similar to that of cell 1 and 2 (overlap is not shown). Sep. soma separation, ∆ori difference of preferred orientation. Scale bar 500 µm