Figure 7.
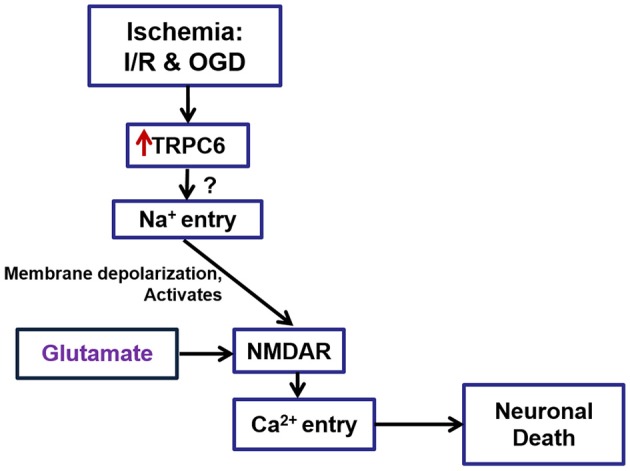
A schematic drawing to show the role of TRPC6 in I/R- and ODG-induced Ca2+ influx via regulation of NMDARs. TRPC6 expression was increased in neurons following I/R in mice brain and OGD in primary cortical neurons. TRPC6 up-regulation following I/R and OGD induced cortical neuronal death may in part through Na+ entry, leading to over-activation of NMDA receptors, and causing an overload of Ca2+. Deletion of TRPC6 protects against cerebral ischemia-induced brain damage in vivo and OGD- and excitatory neurotoxin-induced cell death in vitro. This protection is mediated partially through TRPC6-mediated NMDA pathways.
