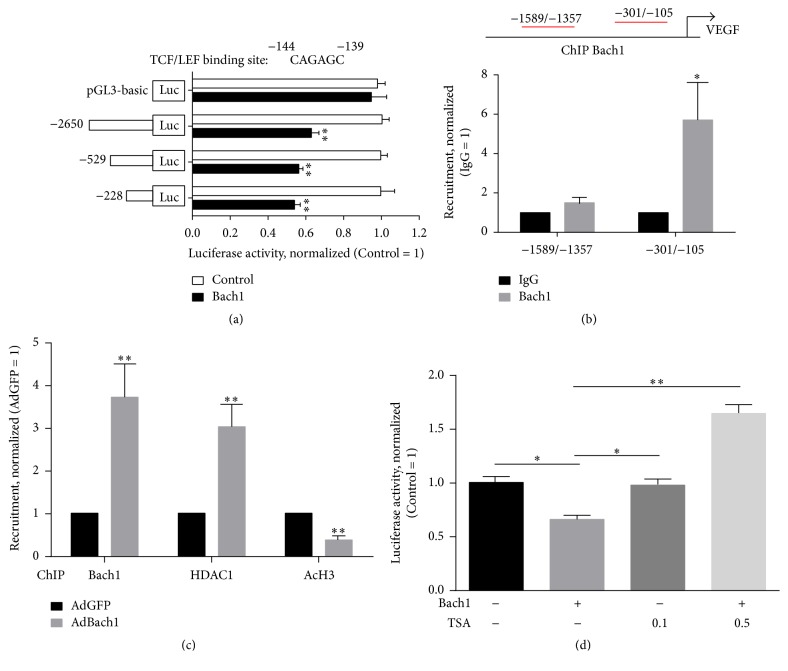
Figure 4.
Bach1 occupies the TCF/LEF-binding site of the VEGF promoter and recruits HDAC1 to the VEGF promoter in HUVECs. (a) Potential TCF/LEF-binding site of the VEGF promoter is shown. Luciferase reporter constructs were created containing the truncated (−2650, −529, and −228) versions of the VEGF promoter; then the VEGF reporter or a pGL3-basic luciferase reporter and β-gal were cotransfected with a Bach1-coding vector or with an empty vector (Control) into HEK293T cells, and luciferase activity was evaluated 48 hours later (n = 3; ∗∗P < 0.01 versus Control). (b) Chromatin immunoprecipitation DNA was isolated with an anti-Bach1 antibody or with a Control IgG antibody, and then quantitative real-time RT-PCR analyses were performed with primer sequences from the indicated regions of the VEGF promoter in HUVECs (n = 4; ∗P < 0.05 versus Control IgG). (c) HUVECs were transfected with AdGFP or AdBach1; then chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed with antibodies against the indicated proteins. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analyses were performed with a primer for the VEGF promoter (−301/−105) (n = 3; ∗∗P < 0.01 versus AdGFP). (d) HUVECs were transfected with AdGFP or AdBach1 and with the VEGF (−228) promoter construct; then, the cells were treated with or without TSA (0.1 or 0.5 μmol/L) for 24 hours and luciferase activity was quantified (n = 3; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01).