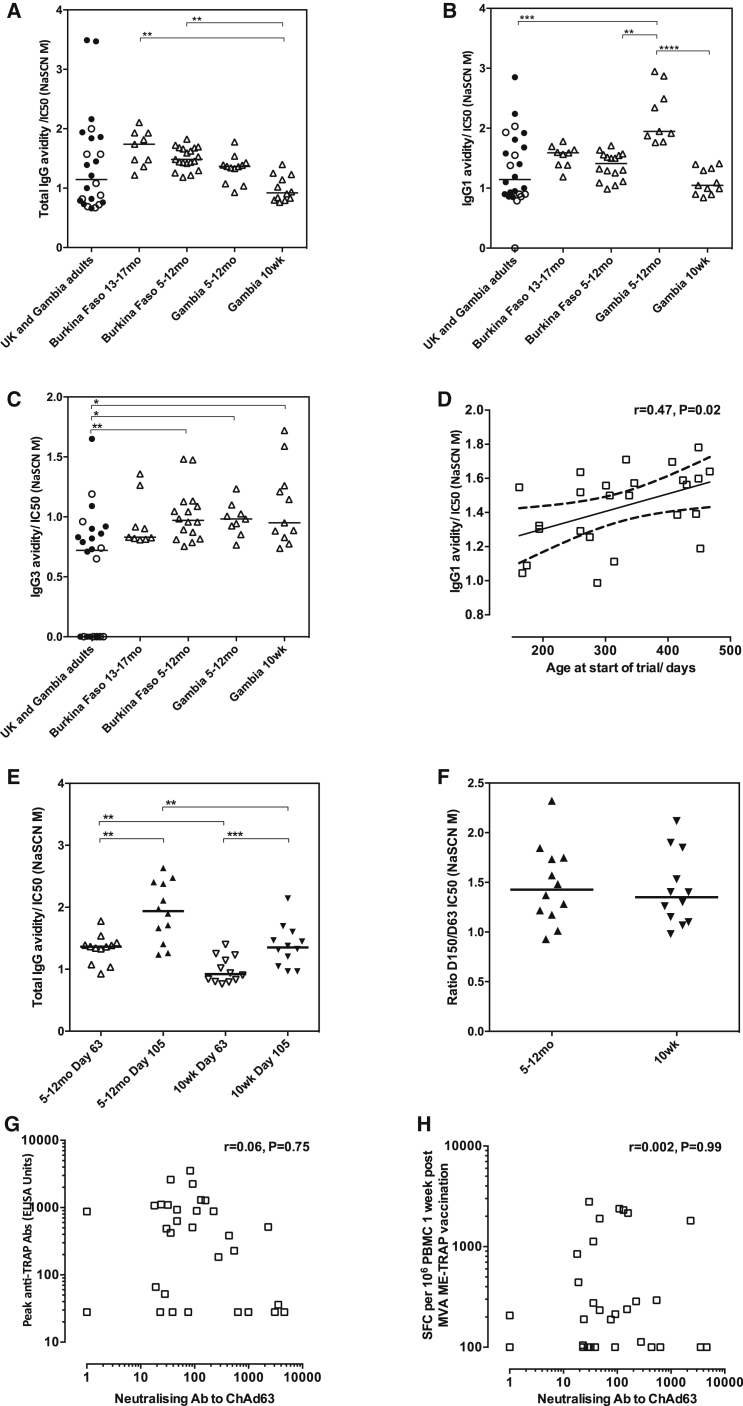
Figure 4.
Antibody Avidity and Anti-Vector Neutralizing Antibodies
(A) Avidity of total IgG (B), IgG1 and (C) IgG3 subtypes in Burkinabe and Gambian younger children and infants (groups 2, 3, and 4) and adults (Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test for multiple comparisons between all groups). (D) Effect of age at first vaccination on IgG1 antibody avidity after boosting in Burkinabe 5- to 17-month-olds (group 4, Spearman’s r = 0.47, p 0.02). (E) Increase in total IgG avidity between 1 and 7 weeks post boost, (p = 0.0015 for 5- to 12-month-olds, p = 0.0010 for 10-week-olds, Wilcoxon matched pairs for comparisons within groups. Mann Whitney test with post-test for multiple comparisons between groups at comparable time points). (F) Change in total IgG avidity between 1 and 7 weeks post boost, expressed as a ratio for each age group (no significant difference by t test). (G and H) Correlations between group 1 neutralizing antibody titers to the ChAd63 vector and peak antibody titers by ELISA and T cell responses by ELISpot, respectively. Spearman’s r = 0.06, p 0.75 for (G) and r = 0.002, p 0.99 for (H). Medians displayed. Kruskal-Wallis tests performed with Dunn’s post-test for multiple comparisons between all groups. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.