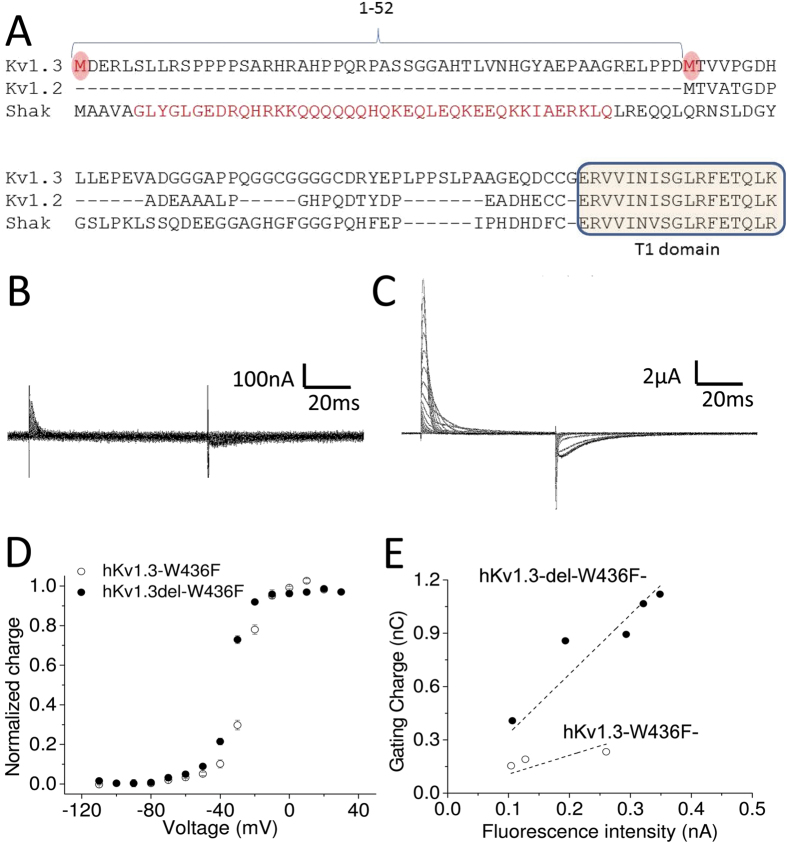
Figure 1. N-terminus of Kv1.3 prevents the expression on Xenopus oocytes membrane.
(A) Amino acid sequence alignments between human Kv1.3 (Kv1.3), human Kv1.2 (Kv1.2) and Shaker K channel (Shak). Two potential start codons are highlighted in red circles in Kv1.3. The N-terminal sequences in Shaker K channel responsible for N-type inactivation is highlighted in red in Shak. The T1 domain is highlighted in light yellow. (B,C) Representative gating currents from hKv1.3-W436F (B) and from hKv1.3-del-W436F (C). (D) Normalized charge as a function of voltage (Q-V) for hKv1.3-W436F (open circles, n = 4) and for hKv1.3-del-W436F (filled circles, n = 8). Error bars indicate standard error of mean (SEM). (E) The total charge as a function of fluorescent intensity for hKv1.3-W436F-mCherry (open circles) and for hKv1.3-del-W436F-mCherry (filled circles). These data were obtained from the same batch of Xenopus oocytes. Each data set was fitted to a linear function (dotted lines). The R2 values were 0.98 for hKv1.3-del-W436F-mCherry and 0.91 for hKv1.3-W436F-mCherry. The linear slopes were 3.4 ± 0.2 for hKv1.3-del-W436F-mCherry and 1.1 ± 0.2 for hKv1.3-W436F-mCherry.