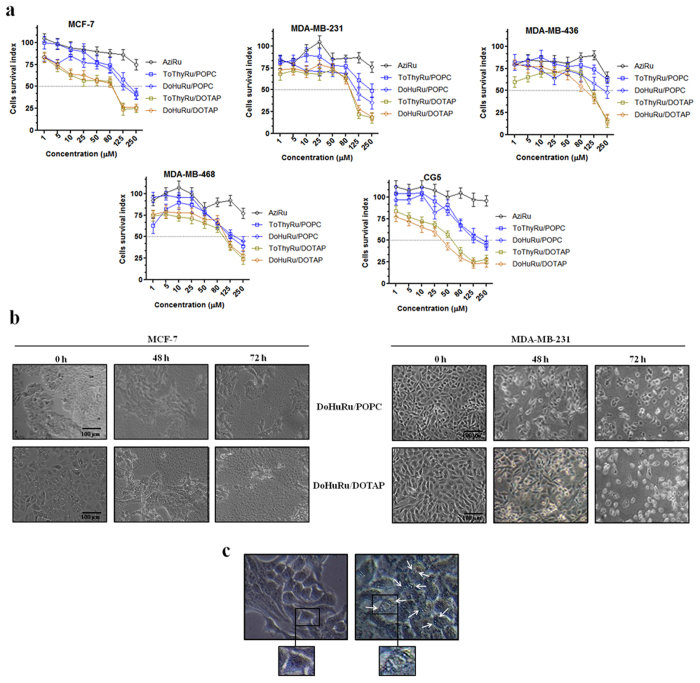
Figure 2. Cell survival index and cytomorphological alterations on cell monolayers.
(a) Cell survival index, evaluated by the MTT assay and monitoring of live/dead cell ratio for MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-436, MDA-MB-468, and CG-5 cell lines following 48 h of incubation with the indicated concentration (the range 1 → 1000 μM has been explored, the one 1 → 250 μM is shown) of AziRu, and of the ruthenium-containing (15% mol/mol) POPC formulations (ToThyRu/POPC and DoHuRu/POPC) and DOTAP formulations (ToThyRu/DOTAP and DoHuRu/DOTAP), as indicated in the legend. Data are expressed as percentage of untreated control cells and are reported as mean of five independent experiments ± SEM (n = 30). (b) Representative microphotographs at a 200 × magnification (20 × objective and a 10 × eyepiece) by phase-contrast light microscopy of MCF-7 (left panels) and MDA-MB-231 (right panels) breast cancer cells treated for 48 and 72 h with ruthenium IC50 micromolar concentrations of DoHuRu/POPC (18.9 and 14.7 μM, respectively) and DoHuRu/DOTAP liposomes (10.3 and 12.1 μM, respectively), showing the cellular morphological changes and the cytotoxic effects on cell monolayers. The shown images are representative of three independent experiments. (c) Representative microphotographs of untreated (left panel) and 48 h DoHuRu/DOTAP treated (right panel) MCF-7 cells by phase-contrast light microscopy at a 600 × magnification (30 × objective and a 20 × eyepiece). DoHuRu/DOTAP (at IC50 concentration) induces the formation of autophagic vacuoles detectable in cell cytoplasm. Inset: higher magnifications of MCF-7 cells before and after treatment.