Figure 6. Sensitivity of affinity mutations in the P4 VH domain to arginine-to-lysine, lysine-to-arginine or asparagine-to-glutamine substitution mutations.
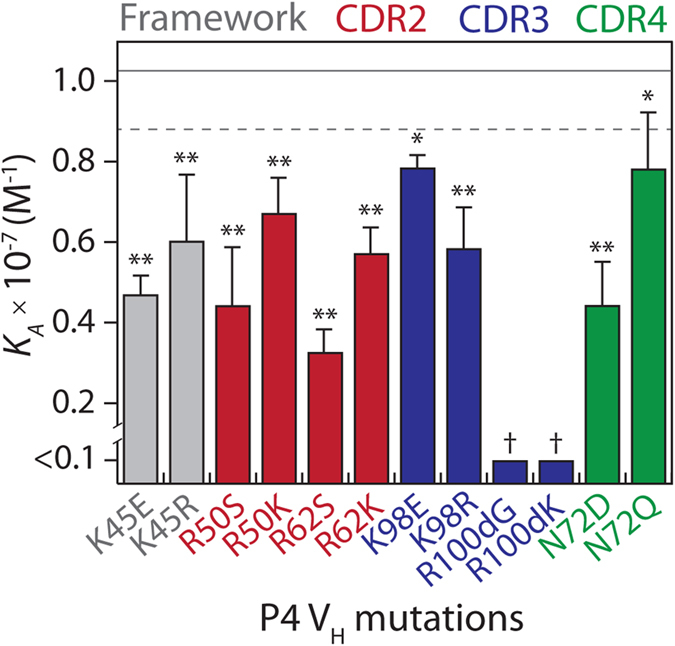
The three arginine mutations in P4 (R50, R62 and R100d) were reverted individually to the wild-type residue (S50, S62 and G100d) or lysine (K50, K62 and K100d). Two lysine mutations (K45 and K98) were reverted individually to the wild-type residue (E45 and E98) or arginine (R45 and R98). Additionally, the asparagine mutation (N72) is located in an N-linked glycosylation site and was mutated to either aspartic acid (wild-type) or glutamine. The association constant (KA) values of the mutants were evaluated as described in Fig. 2. The mutants are highlighted in grey (framework residue), red (CDR2), blue (CDR3) and green (CDR4). The solid and dotted lines represent the average and standard deviation of the P4 VH measurements (n = 7). The measurements for the P4 mutants are averages of multiple independent experiments (n = 4–5), and the error bars are the standard deviations. A two-tailed Student’s t-test was used to judge statistical significance [p-values < 0.05 (*) or 0.01 (**)]. The statistical significance of the R100dG and R100dK reversion mutations (†) could not be computed because of the low affinity of these variants.
