Figure 9. Comparison of the impact of single wild-type reversion mutations on the binding affinity and thermodynamic stability of the P4 VH domain.
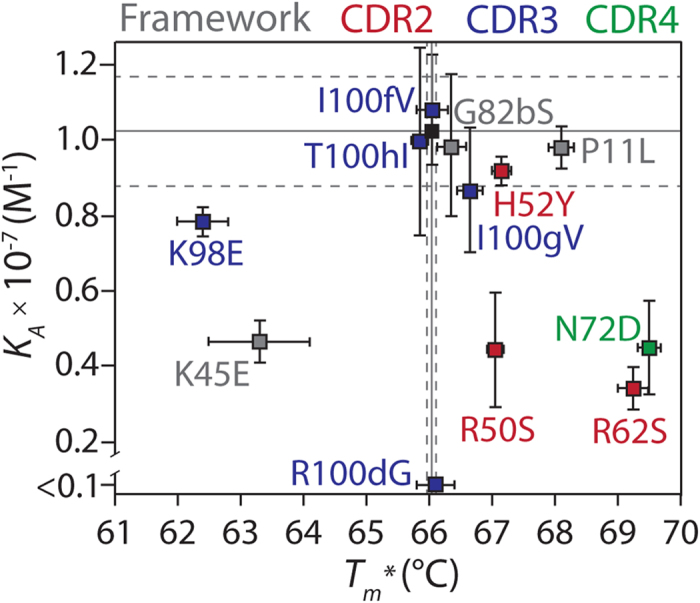
The affinity (KA) and stability (Tm*) measurements for the P4 variants containing single wild-type reversion mutations were evaluated as described in Figs 2 and 3, respectively. Decreases in VH affinity or stability due to reversion mutations signify that the P4 mutations contribute positively to affinity or stability in the corresponding VH domain (and vice versa for increases in VH affinity or stability due to reversion mutations). The reversion mutations are highlighted in grey (framework residue), red (CDR2), blue (CDR3) and green (CDR4). The KA measurements for the P4 mutants are averages of four to five repeats, while the Tm* measurements are averages of two repeats (the error bars are standard deviations). The solid and dotted lines are the averages and standard deviations (respectively) for the original P4 VH domain (seven repeats for the association constant, two repeats for the apparent melting temperature).
