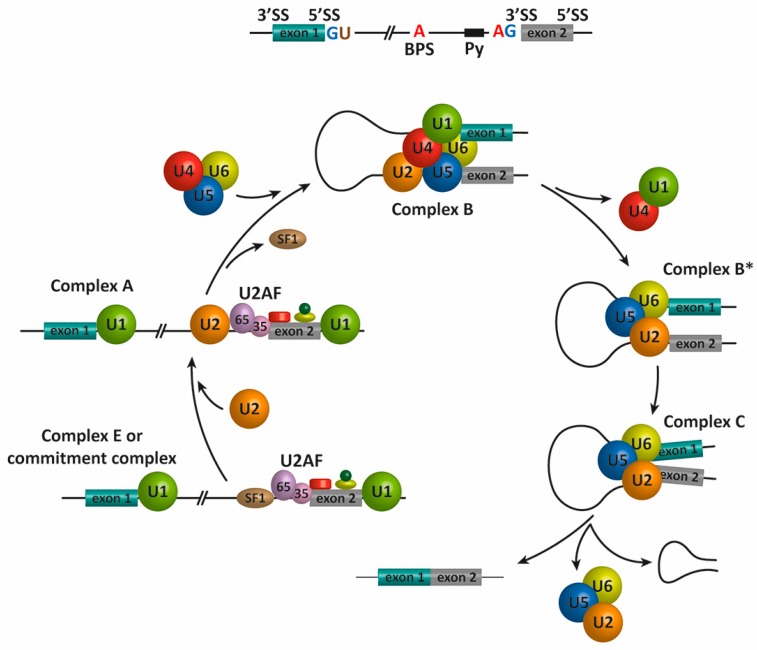
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the spliceosome assembly and pre-mRNA splicing. In the first step of the splicing process, the 5′ splice site (GU, 5′ SS) is bound by the U1 snRNP, and the splicing factors SF1/BBP and U2AF cooperatively recognize the branch point sequence (BPS), the polypyrimidine (Py) tract, and the 3′ splice site (AG, 3′ SS) to assemble complex E [11,12]. The binding of the U2 snRNP to the BPS results in the pre-spliceosomal complex A [13]. Subsequent steps lead to the binding of the U4/U5–U6 tri-snRNP and the formation of complex B [14]. Complex C is assembled after rearrangements that detach the U1 and U4 snRNPs [15] to generate complex B*. Complex C is responsible for the two trans-esterification reactions at the SS. Additional rearrangements result in the excision of the intron, which is removed as a lariat RNA, and ligation of the exons. The U2, U5, and U6 snRNPs are then released from the complex and recycled for subsequent rounds of splicing [16,17].