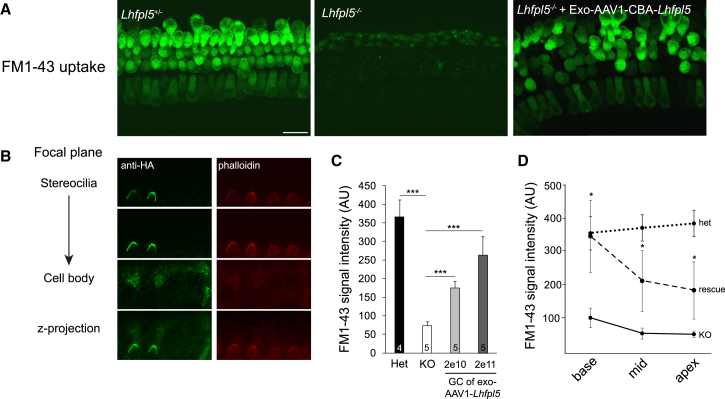
Figure 4.
Exo-AAV1-HA-Lhfpl5 Rescues FM1-43 Loading in Hair Cells in Culture
Lhfpl5+/−or Lhfpl5−/− cochleas (C57BL/6 background) were dissected at P0 and placed into culture for 8 days. Exo-AAV1-HA-Lhfpl5 was added to the culture at P0. At P8, (Tmc2) is no longer expressed and so is no longer an alternate path for FM1-43 loading. (A) FM1-43 loading indicating functional hair cells in control Lhfpl5+/− mice. Knockout transmembrane channel like 2 Lhfpl5−/− animals showed no loading, but loading was evident in the Lhfpl5−/− animals after vector administration (2 × 1011 GCs). Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) LHFPL5 in stereociliary bundles of KO mice after vector-mediated Lhfpl5 gene delivery, which was revealed with anti-HA staining. Hair bundle actin was labeled with phalloidin (red). (C) FM1-43 signal intensity measured with ImageJ. Het, Lhfpl5+/− KO, Lhfpl5−/− GC, genomic copes. Exo-AAV1-CBA-HA-Lhfpl5 administration led to increased FM1-43 signal intensity. ***p < 0.001, t test. Mean ± SEM. (D) FM1-43 signal intensity in Lhfpl5+/−, Lhfpl5−/−, and exo-AAV1-HA-Lhfpl5-rescued Lhfpl5−/− animals (2 × 1011 GCs) in different regions of the cochlea. *p < 0.05, t test. Mean ± SEM.