Fig. 1.
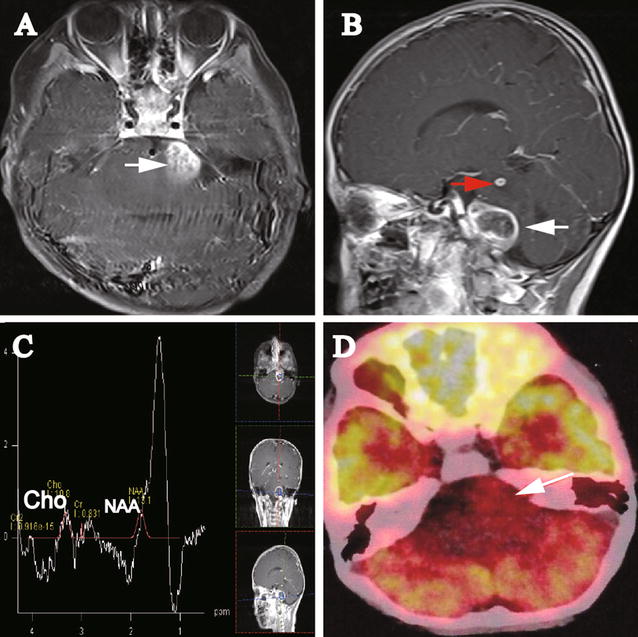
Images of the initial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography–computed tomography (PET–CT) on Oct 8, 2015 for the 5-year-old girl with multiple posterior fossa lesions. A Axial gadolinium-enhanced MRI displays a lesion (2.0 cm × 2.6 cm; white arrow) in the cerebello-pontine angle (CPA). No relatively clear margin was observed between the lesion and the pons. B Sagittal gadolinium-enhanced MRI shows two lesions. The upper left pontine lesion (0.5 cm × 0.6 cm) was significantly gadolinium-enhanced with relatively clear margin (red arrow). From the sagittal view, the CPA lesion (white arrow) seemingly demonstrates clear boundary to the pons. C Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) of the lesion shows a decrease in choline (Cho) and N-acetyl aspartate (NAA). D PET–CT image demonstrates a hypometabolic lesion (white arrow) in the left side of the CPA
