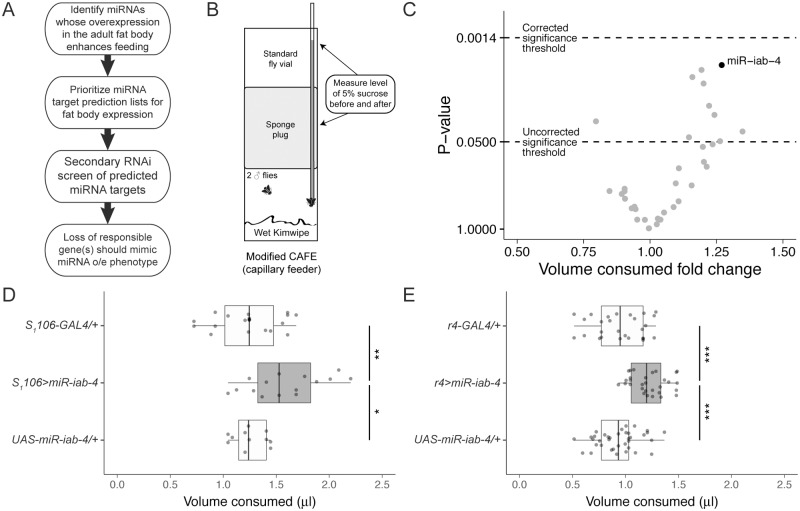
Fig 1. Primary genetic screen shows overexpression of miR-iab-4 in the adult fat body increases feeding.
(A) Flowchart explaining our two-tiered microRNA (miRNA)-based screen for fat body modulators of feeding. (B) Schematic of the modified capillary feeder (CAFE) assay. (C) Summary of the primary miRNA overexpression screen. Each dot represents the feeding of S1106-GAL4 driving the expression of one UAS-miRNA in the fat body. The feeding fold change versus the heterozygous S1106-GAL4/+ control plotted against the p value as determined by a Student’s t test. Significance thresholds, both uncorrected and corrected for multiple comparisons (Bonferroni method), are indicated. See S1 Table for a complete list of UAS-miRNA lines with their feeding fold changes and resulting p values. See S1 Fig for a ranked bar plot showing the mean feeding for all lines in this primary screen. (D and E) Fat body-specific overexpression of miR-iab-4 using (D) the RU486-inducible S1106-GAL4 (n = 11–20) and (E) the constitutive r4-GAL4 (n = 27–37), both in gray, increase feeding compared to heterozygous controls (white). Underlying numerical data for this figure can be found here: http://dx.doi.org/10.5061/dryad.8hm82.