Figure 5. IGF-1R/AKT signaling is critical for cancer cell dormancy in a reversible pancreatic tumor model that is based on the conditional expression of c-MYC as the primary oncogenic driver.
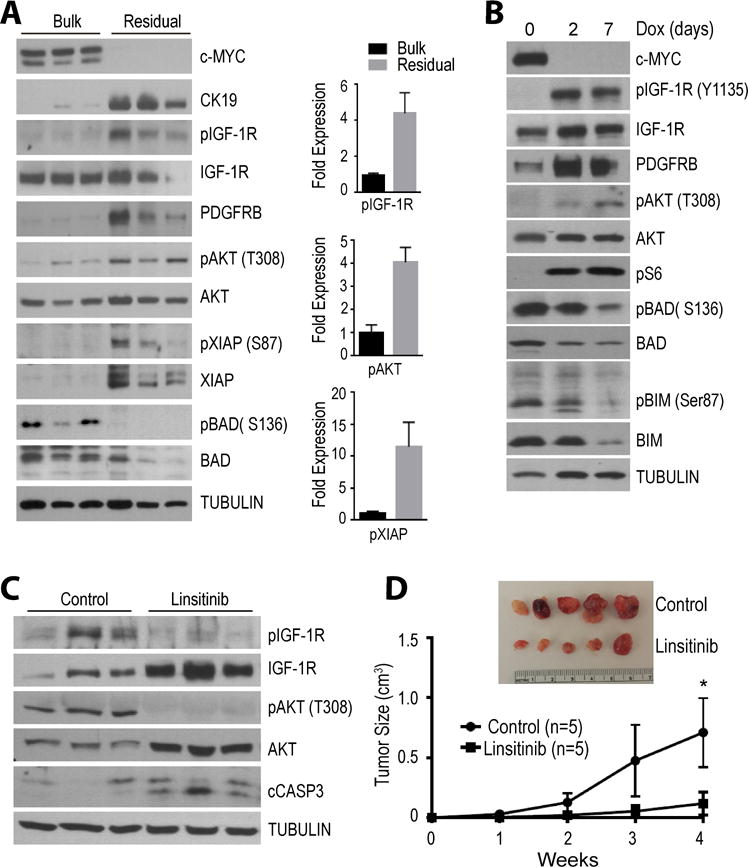
A. Immunoblot analysis comparing the expression and activation of IGF-1R, AKT, and the levels of downstream cell survival/death effectors between bulk tumors and residual cancer tissues in vivo. Bar graphs show Image-J quantification of selected protein bands. All data are represented as mean ± SEM; * represents P<0.05. B. Activation of the IGF-1R/AKT signaling in cultured pancreatic cancer cells following the doxycycline (Dox)-mediated downregulation of the oncogenic driver c-MYC. C. Validation of the pharmacological inhibition of IGF-1R and AKT signaling as well as activation of cleaved caspase 3 (cCASP3) in residual cancer cells in vivo. D. Tumor growth curves comparing cancer recurrence following re-expression of exogenous c-MYC between controls and animals that were treated with the IGF1-R inhibitor linsitinib.
